Save flat 35% on Assignment
Read this academic research paper example & explore New Assignment Help USA's full range of academic writing services designed just for you—because great work deserves the perfect partner. Flip the page and let’s make it happen!
Dissertation Title: Pricing And Customer Segmentation For Business Development, A Competitive Economic Growth Between Uber And Ola
Ride-sharing has experienced significant development in recent years because of advances in mobile technology and connectivity. India represents a particularly lucrative market opportunity because of its positive demographic structure and rapid smartphone penetration. Given the vast and various populace in both metropolitan and country regions, viable valuing systems and client division models are fundamental for stages like Ola and Uber to be productive and target different client gatherings. As the contest between these opponents increases, thinking about the qualities and impediments of each way to deal with situating and valuing its merits.
Ola began their journey in India in 2010, three years before the worldwide monster Uber entered the market. The two organizations have continued forcefully contending in huge and second-level urban communities since then. Massive funding has fueled growth, with Ola raising over $3 billion and Uber putting in over $1 billion for India expansion. The two companies offer various services, including ride-hailing, food delivery, micro insurance, vehicle leasing, and more (Vinod & Sharma, 2021). Ola's local knowledge and Uber's global reach and technology create a near-duopoly situation where the two companies control more than 90% of the ride-sharing market share in India.
The problem statement essentially facilitates to identification of the discrepancies that have been addressed in the research of the chosen topic. This research would investigate the positive and negative determinations in the commercial automotive industry. The significance of customer segmentation, service modification and pricing strategy would be useful to secure and persist the business growth. It helps predict future operations and financial growth and reduces the chances of risk threats.
The research aim is a very significant aspect of defining the main matter of the research. This research aims to identify the performance of OLA and Uber to achieve success in customer segmentation through pricing and quality modification. The research would thereby, have been useful for providing the company's policies in respect to pricing as per the customer segmentation of the companies.
This is the section of the first chapter of the dissertation where the objectives of the research are to be established. This section of this initial chapter facilitates the limiting of the research to a certain by providing objectives to focus on. Therefore, the objectives for this research regarding ridesharing companies like Ola and Uber’s pricing policies and customer segmentation have been stated.
Thus, the objectives cover a wide range of scope of the companies Ola and Uber. Thereby, the focus will also be on the financial and corporate social responsibility aspect of the as well (Sharma, 2023). Further, the customer environment and employee growth are also very significant components of consideration for the companies and thereby, the objectives have been formed in such a manner that all these are covered.
This section of the initial chapter of the dissertation is to provide the questions that are raised for the research. The research questions are essentially structured following the research aim and objectives. This is to connect the questions to the objectives to provide more clarity to the findings of the research (More, and Rakshit, 2020). Thus, the questions based on the pricing strategy and customer segmentation of ridesharing companies like Ola and Uber are as follows:
Thus, the questions that rea presented are to be discussed in detail in the analysis chapter of this dissertation.
This study on pricing strategy and customer segmentation aims to provide data-driven, actionable insights for Ola, Uber, and other players in the collaboration economy. Increasing competition has put pressure on margins and called into question the sustainability of the business. The results of this study will support companies in making strategic decisions regarding market positioning, pricing of services, optimizing spend, and responding to changing consumer preferences (Surie, 2020). The study also highlights areas where governments can intervene politically. Price regulations and driver benefits. This paper also aims to advance academic research on the sharing economy by filling the gap in the academic literature on ride-sharing economics in emerging economies such as India.
The results of this study will complement both the hypothesis and the rational information. On the hypothesis side, the relationship between valuation methods, customer sectors and market-oriented methods in the sharing economy will be better understood. The findings and recommendations will help Ola, Uber, and new entrants agree on more informed decisions regarding operational calculations, buyer orientation, and maintaining profitability. Policymakers can also benefit by highlighting customer preferences, bottlenecks, and support opportunities (Sinha et al., 2021). This suits large-scale government activities involving development implementation, such as smart cities and Digital India. Therefore, audits affect various partners beyond the actual organization.
(Source: Self-created)
This is the first chapter of the dissertation and thereby, the purpose of the chapter is to establish the factors of research that are to be focused on during the conduct of the research. The aim of the research makes clear the targeted conclusion this research would aim at finding and achieving by the end of the analysis chapter. Therefore, the objectives have facilitated to signify the areas of research requirement for the successful complement of this dissertation. The rationale of the topic considered for the research and the significance if this study has also been mentioned. Thus, the initial chapter has provided a glimpse of what the dissertation would be based on.
The literature review forms the basis for conducting the research by providing an overview of existing knowledge about the research topic and objectives. In this study on pricing strategies and customer segmentation approaches used by ride-hailing platforms Ola and Uber, the literature review helps identify essential themes and gaps that require further investigation. This chapter brings academic perspectives on the ride-sharing industry, pricing models, customer profiling and segmentation techniques related to service markets such as Ola and Uber. Both theoretical concepts and applied case studies are covered to ensure a learning link between science and practice.
As this is an emerging field, the review includes transportation journals and literature on marketing, technology adoption, segmentation, and the sharing economy. The literature review provides the background and rationale for the research questions posed in Chapter 1 by evaluating existing research on factors that enable competitive pricing and segmentation. This finding forms the basis of the conceptual framework adopted for primary data collection and analysis, Ola and Uber filling the knowledge gap. The main points of the literature are summarized not only to present current knowledge but also to highlight opportunities for further research, thereby creating a platform for the current research.
According to Godbole and Deshmukh, 2020, the journal article investigates the influence of demographic factors such as age, income, and education on customer perceptions of app-based taxi services in Nagpur, a second-tier city in India. This provides a useful link to the focus of our paper, which focuses on investigating the pricing strategies and customer segmentation models used by ridesharing category leaders Ola and Uber across India.
In particular, the study's investigation of differences in service perceptions between different demographic groups is very similar to the assessment of how best for mobility platforms to classify and target specific customer segments. ANOVA analysis reveals significant differences in perceptions based on variables such as occupation, education, and income level. Companies like ANI Technologies (Ola) and Uber India Systems have segmented pricing policies and advertising tailored to each user profile's needs and sensitivities rather than relying on a single, homogeneous service. This is directly aligned with the need to design campaigns—the one-size-fits-all approach for all user profiles.
For example, this magazine study found that employees prioritize driver behavior, ease of payment, and service packages. In contrast, students prioritize discounts, wallet promotions, and app convenience. It has been shown that These two subgroups are both highly relevant target categories for rideshare companies and have different needs and
behaviours regarding peak and off-peak usage, average spending, and trip purpose.
Therefore, they will respond differently to price incentives such as office commuter cards and campus discount vouchers. Similar demographic cluster analysis applied to the rich ride usage and transaction data available through Ola and Uber apps can guide the design of customized customer segments and their associated pricing.
In addition to demographics, the financial statement also analyzed service aspects such as taxi cleanliness, amenity availability, and GPS usage, and driver perceptions of these attributes were linked to driver satisfaction. These complement the magazine's demographic perspective. Combining drivers' perceptions of this value-added attribute with their actual Ola and Uber usage and transaction patterns can identify and prioritize value-oriented customer segments focused on service quality and price. For example, travelers to an airport have certain expectations about whether their driver is familiar with the route and can be relatively price-insensitive during busy periods. Grouping the app's user data along these value parameters related to service aspects will highlight attractive yet underserved niches.
Therefore, the core of this journal article, investigating changes in customer perceptions, usage preferences, and satisfaction with taxi services across demographic and value-based characteristics, is the core area of this paper: segmentation. This has important implications for methodology and pricing decisions. This is a template for rideshare companies to analyze different user profiles and tailor differentiated product and pricing interventions to maximize customer lifetime value for each identified target segment.
Finally, this journal article presents an approach focused on investigating differences in service perceptions and expectations across user segments and a differentiated targeting and pricing approach, i.e. competitive. It has valuable implications for developing strategies supporting sustainable growth in India and the still-developing ride-sharing market.
According to Dsouza, W. 2019, the authors' research explains how transport startup Ola Cabs leveraged app-based digitization to revolutionize India's taxi industry, rapidly scaling up and capturing a dominant market share. This relates directly to the paper's focus on how pricing strategies and customer segmentation approaches have driven the success of mobility platforms such as Ola and Uber.
Specifically, the authors argue that Ola leverages mobile technology to connect urban commuters and auto drivers reliably and conveniently, thereby addressing the shortcomings of India's unorganized taxi industry (low reliability). They highlight how they took advantage of poor service, lack of transparency, overcharging customers, etc. This is reflected in industry leaders like Ola and Uber leveraging data-driven, customer-centric solutions to unlock mass-market opportunities that traditional transportation models could not tap.
(Source: Dsouza, W., 2019)
For example, the study found that ease of access through mobile apps allowing taxis to be booked at the "push of a button," lower fares per kilometre, and increased transparency through GPS tracking are among the shows they have tapped into the middle-class market.
Things for commuters used to be too expensive. They are leveraging digitalization to unlock new sources of value. Insights like these can help drive optimized pricing and advertising for ride-hailing companies targeting different consumer segments based on willingness to pay and usage patterns. This emphasizes the intention of the paper to explore approaches.
This analysis explores how Ola can build its service by combining the benefits of existing modes of transportation, such as quick car connectivity and low bus fares, while eliminating pain points such as booking, payment, and tracking. It also shows whether it has been adjusted. This shows the benefits of a suitable customer segmentation model that allows Mobility His platform to select the most attractive elements along the value chain for differentiated positioning.
Additionally, visual frameworks such as the Strategy Canvas, Four Action Grid, and Value Curve Diagram provide tools for mapping the impact of pricing factors and service attributes on value offerings and decisions related to competitive differentiation. Although this analysis focuses on Ola here, it forms the core of evaluating the price segmentation relationship between Uber and Ola as part of my dissertation research.
Therefore, the essence of this journal article is to show how digitalization has overturned the current mobility paradigm and opened up new frontiers of growth. Examples include aggregators such as Uber and Ola. Perspectives such as incentivized pricing, customer focus, and leveraging technology to exploit market opportunities play into the strategies these industry leaders adopt as they compete for leadership in India's emerging ride-sharing space.
According to, Sharmin, F., 2021, the attached journal article explores how the coronavirus pandemic has affected mobility disruptor Uber and is directly related to dissertation research on ride-hailing companies' pricing and segmentation strategies. Specifically, the 80% drop in Uber rides worldwide at the height of lockdowns highlighted in the paper is due to the supply and demand faced even by new entrants to the category like Ola.
This reflects the instability of these segments will continue to evaluate their audiences and understand changes in usage opportunities, even when market conditions have significantly eased due to external shocks such as COVID-19 and competition, demonstrating the benefits of adjusting advertising incentives.
(Source: Sharmin, F., 2021)
For example, people may be more willing to pay for a ride to an airport that requires a longer travel time, even if there are general limits on discretionary spending. Business commuting may show early signs of post-pandemic recovery compared to leisure travel. Grouping users based on value and behavioral metrics enables customized policy responses. Uber's job losses and revenue declines highlight the challenge of balancing driver economics, service prices, and consumer value. The ability to dynamically adjust pricing models becomes even more critical in turbulent situations.
The regional focus of this study is South Asia, which is also consistent with the paper's focus on India as a strategic market, where players serve consumers ranging from the middle class to businesses. The fares and types of taxis need to be adjusted to provide. Furthermore, the competitive dynamics highlighted in his paper on how local competitors imitate Uber's model emphasize the value of continuously improving innovation and service differentiation as a buffer against imitation.
This makes customized customer experiences based on rich usage data even more critical. Overall, this article's perspective on how shocks like the coronavirus impact the operations and growth strategies of innovative companies like Uber is mainly similar to the paper's focus on configuration and segmentation approaches. The pandemic has been a turning point for the mobility sector, reshaping market size, consumer preferences, and the limits of the adaptability of online platforms.
This paper provides a framework for assessing opportunities such as audience retargeting, differentiated advertising, and driving service innovation to customize for sustainable value creation amid disruption [Referred to Appendix 2].
According to Vatal, A. 2023, in the article published in the International Journal of Research in Engineering, Science, and Management, the author discusses Uber’s transformative impact and mentions the auto-rickshaw industry in Pune. The study, conducted in 2023, focuses on the consumer perspective and provides valuable insights into the evolving dynamics of transport services in this Indian city. The author first tends to the general subject of interruption brought about by Uber's entrance into the auto rickshaw market. The title establishes the vibe for looking at how this technology-driven stage has reshaped the conventional auto rickshaw scene and features the significance of the customer's voice in understanding this change in perspective. The strategy utilized by Vatal includes gathering and dissecting information from buyers in Pune to acquire a nuanced comprehension of their encounters and discernments.
(Source: Vatal, A., 2023)
The review uncovers that Uber's increase affects different parts of the auto rickshaw business. Through meetings, reviews, and other exploration devices, the creators catch the opinions of customers who have embraced Uber's administrations or who stay faithful to customary auto rickshaws. The discoveries uncovered a scope of conclusions, from excitement for the comfort Uber gives to worries about its effect on neighborhood auto rickshaw drivers. Vital handily presents these alternate points of view, giving the peruse a far-reaching outline of the complicated connection between technology-driven development and laid-out privately based transportation administrations.
This article not only gives an outline of the ongoing situation yet in addition brings up provocative issues about the future improvement of the auto rickshaw business in Pune. The conversation segment thinks about potential methodologies for concurrence or transformation, perceiving the requirement for harmony between embracing mechanical advances and protecting the livelihoods of customary specialist co-ops.
This writing is a decent book that reveals insight into the complex transaction of development and custom in the vehicle administration area. Vatal's top-to-bottom exploration philosophy and smart examination add to a complete comprehension of how customer viewpoints have been and are being molded by the developing elements of the auto rickshaw business in the computerized age [Referred to Appendix 3].
According to THAPA, G., 2020, the journal article provides valuable insights into consumer behavior and perception towards app-based taxi services in India, which could inform pricing and segmentation strategies for companies like Ola and Uber. This study, which targeted 100 respondents from major cities, will help understand the preference factors of different target categories such as students, professionals, and retirees. The analysis found that service aspects such as safety, affordability, and accessibility are more critical to city commuters than mere cleanliness and comfort. This is consistent with the strength of mobility apps in providing differentiated services tailored to users' needs.
For example, services like Ola Auto, which offers cost-conscious everyday rides and premium rides for businesses, pay a premium for luxury commuting benefits. Commuters' willingness to pay more for nighttime security highlights the potential for dynamic segmentation. The paper also notes that some older adults concerned about technology are underserved, expressing frustration at not having options other than apps. This age group will respond to promotions that emphasize booking assistance and additional driver verification over app functionality.
Given that Ola is cost-sensitive, it must build trust to steer them away from public transport. Additionally, the gender distribution of respondents reflects the paper's focus on women's safety and customized products such as Ola Pink. The author’s findings on female driver preferences and sexual harassment risks highlight the need for appropriate safety features, pricing, and positioning to grow this segment. Partnerships with women's groups will increase penetration.
Additionally, analysis linking income level to willingness to pay more confirms the value of grouping users based on their propensity to absorb price increases during peak demand. Higher-income groups remain relatively price-inelastic and may be eligible for subscription plans and loyalty benefits. The paper, therefore, provides a suitable background to segmentation strategies and related pricing approaches from a demand perspective and complements papers focused on firms' pricing and product mix decisions. Consumer insights into brand presence, technology adoption, and response to promotions can further refine Ola and Uber's dynamic growth plans in India.
According to Saxena, 2019, the journal article provides highly relevant insights into how Uber leverages digital technology and real-time data analytics to disrupt traditional taxi services in India. This aligns with the paper's focus on how app-enabled mobility platforms like Uber and Ola have leveraged digitization and analytics to reshape urban transportation through innovative pricing strategies and customer segmentation approaches.
Specifically, the authors leverage the rapid proliferation of smartphones and mobile internet connectivity across India to address the unreliability of taxi availability, lack of transparency in fares and ride status, and prices. Explains how Uber's model helped overcome critical consumer issues such as rising prices in the city where it was used.
Key features such as GPS-based tracking, digital payments, and real-time automated ride matching addressed commuter needs and complaints that incumbent taxi companies had long ignored. These perspectives suggest that the personalized, technology-centric experiences enabled by aggregators such as Uber and Ola represent a fundamental paradigm shift from the standardized and chaotic status quo of public transport and additional taxi services. This confirms that Platforms like Ola and Uber are poised to meet new consumer expectations for hyper-personalized, contextual and seamless urban mobility interactions by leveraging the power of mobile apps and data science.
(Source: Self-created in MS Word)
Additionally, this paper leverages digital interfaces and a continuous stream of detailed location and usage data to balance demand and supply dynamically through price increases. Availability optimization emphasizes the critical role of applying advanced data science techniques to analyze individual driver usage patterns, preferred routes, time preferences, and more; companies can optimize asset utilization and driver and partner revenue in real-time. It was also conducted through BGG metrics, which provide insights into the author’s aim and objectives. This highlights the key benefits of data-driven operations. This important feature is also considered in the literature research from the perspective of target customer segmentation, price optimization, and promotion personalization.
Additionally, the real-time transparency mechanisms enabled by the Uber app platform create powerful network effects that self-amplify trust, security, and continued exponential user growth. Mapping customer travel frequency and purpose (commuting, airport, etc.) based on parameters such as time of day, neighborhood, route, etc. makes it easy to develop highly customized incentive systems and promotions to encourage habit formation. It will be an essential consideration.
The article describes how platforms like Uber have succeeded in establishing app-based on-demand mobility by integrating digital tools, real-time data, and analytical methods into urban transportation. The innovative focus on digitally disrupting the traditional taxi value chain reflects how India's ride-sharing unicorns like Ola and Uber are combining innovation and deep insights into local consumers to gain market advantage. This reflects the paper's focus on examining whether the continued focus on users, enabled by data analytics, supports the company's competitive advantage and growth trajectory.
This article also highlights opportunities for advancing social participation by tracing how Uber's model has bridged the mobility gap in large cities once poorly connected to public transport and taxis. Platform innovations supporting first-time and non-technical smartphone users can expand the addressable market. Location-specific use cases, such as facilitating airport ride pooling, highlight the potential. It can also expand the funnel by partnering with governments and integrating with public transportation.
The paper, therefore, provides contemporary evidence and critical insights into how the Uber paradigm has redefined urban mobility through digital transformation and data-driven innovation. The focus on leveraging technology to shape experiences and operations focuses on a technology-enabled, customer-centric pricing and segmentation approach to achieve success and sustainability in the Indian market.
According to Ramasamy et al. (2021), the journal article investigates the factors influencing customer satisfaction and choice of taxi service providers in the Indian city of Bhubaneswar. This provides a helpful background for the paper to focus on the pricing strategies and customer segmentation approaches used by ride-hailing platforms such as Ola and Uber to gain a competitive advantage.
Specifically, this study analyzes how service reliability, quality, cost, and driver behavior influence commuters' preferences among app-based taxi brands. It explores how personalized experiences, dynamic pricing, and positioning influence consumer behavior in target segments defined by demographics, willingness to pay, reasons for usage, etc. This reflects the intention of the paper to the results highlight that service availability, safety, discounts, and driver behavior are essential factors in brand selection. This will guide mobility companies on segmentation based on parameters such as women's safety and risk tolerance and customization for usage situations such as airport transfers and overnight travel where reliability is paramount to provide incentives. Gender differences in brand affinity highlight the potential for targeted positioning.
Additionally, this analysis focuses on continuously improving aspects such as clean vehicles and driver certification to positively impact customer experience, which is a critical factor in pricing power and willingness to pay. This paper focuses on investments that are also being made in technology capabilities that build trust and support reputation, such as GPS tracking and digital payments.
The document, therefore, provides a suitable background on how service aspects related to reliability, and economic and behavioral factors influence the choice of commuting options in India. Taxi companies like Ola and Uber must adapt, adjust, and innovate to offer services that benefit India's diverse urban consumer base while maintaining a competitive advantage. It complements the paper's focus on pricing and segmentation strategies [Referred to Appendix 4].
The research paper titled "Capital Market Forecasts in Indian Internet Commerce" by D'Souza and Dev explains the complex relationship between India's Internet commerce sectors. This research provides valuable insight into the broader realm of economic dynamics and market forces in technology-driven contexts. D'Souza and Dev's study of capital market predation provides a basis for understanding the complex dynamics that often affect competitive industries. Although the focus is on Internet commerce, this study's methodology and analytical framework may provide potential parallels and inspiration for studying similar phenomena in the ride-sharing field.
The authors provide a comprehensive study of market trends, investment patterns, and strategic moves by leading companies, contributing to a nuanced understanding of how financial dynamics shape the competitive environment. Although the subject matter may vary, as the paper's title suggests, the methods and insights presented will be valuable to researchers seeking to decipher the economic complexities associated with business development and competitive growth.
Additionally, this article raises thought-provoking questions about regulatory considerations and strategic responses in light of marketing forecasts. These considerations may be relevant to the literature's pricing strategy and customer segmentation research, providing a broader perspective on how economic factors influence business decisions. This provides a solid foundation for understanding economic forces and market dynamics, and potential insights and methodologies that can be useful in studying pricing strategies and customer segmentation in the competitive environment of ride-hailing platforms such as Uber and Ola.
|
Description of Variables |
|||
|
|
|
Years Available |
Sample Size |
|
S/N |
Panel A: Key variable links between pricing and competitive dynamics |
|
|
|
1 |
Price-Cost Margin |
2010-2020 |
50 firms |
|
2 |
Market Share |
2010-2020 |
1000 observations |
|
3 |
Entry |
2010-2020 |
50 firms |
|
4 |
Advertising |
2010-2020 |
50 firms |
|
5 |
R&D |
2010-2020 |
50 firms |
|
6 |
Capacity |
2010-2020 |
50 firms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Panel B: Other endogenous variables |
|
|
|
1 |
Leverage: Ratio of long-term debt to Total asset |
2010-2020 |
50 firms |
|
2 |
Company size: Total asset |
2010-2020 |
50 firms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Panel C: Performance variables |
|
|
|
1 |
Return on Assets: This study measures ROA as the ratio of operating income before depreciation to end-of-year total assets(Barber & Lyon, 1996) |
2010-2020 |
50 firms |
Table 1:Description of Variables
(Self-created in MS Word)
Pricing strategy and client division do not work in separation yet are firmly connected with cutthroat elements between organizations. Consequently, Porter's Five Forces (PFF) gives this review a suitable hypothetical focal point. Created by Harvard College researcher Michael Doorman, the film investigates the bartering force of purchasers and providers, the danger of substitutes, and competitive connections to decide an industry's productivity and appeal.
The use of PFF shows how Ola and Uber's evaluating and division approaches are affected by variables, for example, aggressive movement, worker needs, driver associations, and the rise of public vehicles (Liu & Kim, 2022). For example, price hikes by new entrants and driver withdrawal due to low wages have forced a review of fares and target groups. This model also helps to contextualize research findings across ridesharing environments.
In addition to PFF, the customer pyramid provides a valuable framework for service strategy. It is widely used for segmentation analysis in the hospitality, transportation, and digital economy sectors. The pyramid identifies five customer tiers based on profitability and loyalty, from high-volume customers at the base to high-value partners at the top.
Mapping Uber and Ola's customer categories into a pyramid model allows us to assess which segments are currently prioritized through discounts and promotions and which provide stability through repeat transactions (Muralidhar et al., 2022). The research can then derive relationships between customer tiers and optimal pricing strategies. The visual nature of the model also effectively conveys how the platform segments different consumer groups, from mass-market casual drivers to corporate customers.
Therefore, PFF and customer pyramid provide a relevant interdisciplinary theoretical and conceptual model to study Indian ride-hailing services, competitive environment, and segmentation considering research objectives. Anchoring the study in an established scientific framework increases the analytical generalizability of the results. Porter's Five Forces further addresses the application of these theories and models to research situations and identifies the critical structural forces that influence competition and shape the ride-sharing market environment in which Ola and Uber operate. It provides a structured approach to determining the Mapping of the competitive relationship between two dominant companies and the relationship of bargaining power with customers, drivers, regulators, and new alternatives such as public transport, providing a comprehensive perspective (Venkatesh, 2022). By overlaying a company's pricing strategy and segmentation model with this industry analysis, it can derive descriptive and predictive connections to its business approach.
Complementing this scan of the external environment, applying the customer pyramid to services within an organization provides a conceptual blueprint for categorizing different customer groups based on revenue potential and loyalty. The pyramid visually represents the breadth of transacting users at the base and the avid spenders as it moves up (Mukerji & Roy, 2019). Which segments are currently underserved in price by delineating the different customer groups such as students, office commuters, and airport travelers that Ola and Uber are targeting at these levels? It also becomes more accessible to assess where fierce competition overlaps. Linking price incentives and promotions to the pyramid levels shows how the platform strives to move users along the loyalty spectrum.
Although the literature review covers essential aspects of ridesharing dynamics, pricing theory, and segmentation approaches, there are some obvious gaps that this paper aims to fill.
First, academic research on the real-world ridesharing economy focuses disproportionately on Western markets such as North America. However, at the end of the day, an emerging market like India requires a targeted assessment, where consumer preferences, transportation infrastructure and competitive intensity vary widely.
Second, the literature tends to be concentrated within disciplinary silos. For example, research on pricing strategies is still limited to financial journals and has little relevance to segmentation models from a marketing perspective (Wilson & Mason, 2020). This study takes a multidisciplinary approach, including business, management, and technology implementation perspectives.
Finally, and most importantly, there is limited academic research on the interaction between pricing and segmentation decisions for platforms such as Uber and Ola. Although both factors have been studied separately, the relationship between the two and how pricing policy and customer clustering influence each other has received little attention (Velmurugan et al., 2019). In reality, this is a significant knowledge gap because important decisions regarding promotional offers and loyalty programs directly influence the selection of target markets and vice versa.
This paper aims to address these gaps by providing new scientific insights specific to the intersection of ride-hailing, pricing strategy, and customer segmentation in India's unique context. A holistic approach can uncover new relationships between pricing and segmentation while considering external competitive, macroeconomic and regulatory variables surrounding the sector (Kadam & Kadam, 2022). Platform-specific observations have implications not only for taxi aggregators but also for the broader sharing economy.
(Source: Self-created in MS Excel)
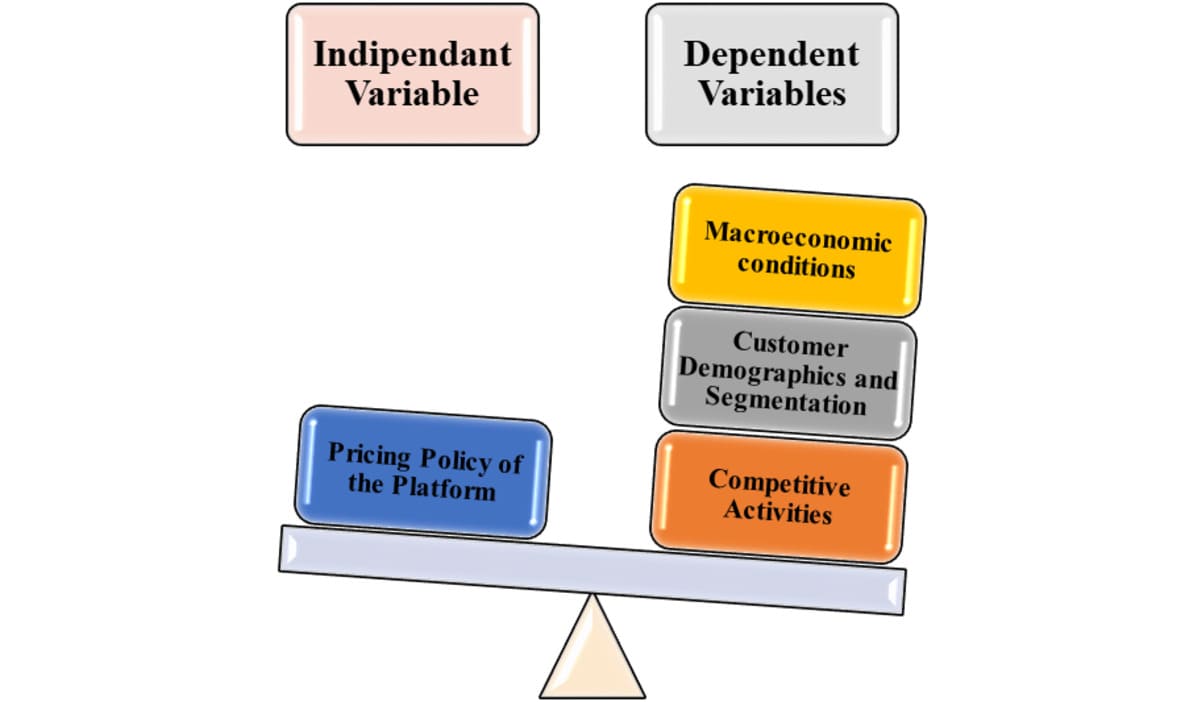
Based on the literature review and discussion of appropriate theories and models, the following conceptual framework guides the literature analysis on ridesharing pricing strategies and customer segmentation. The primary dependent variable is the pricing policy of the platform, which covers special offers, discounts, and dynamic prices of taxi companies such as Ola and Uber (Sehrawat et al., 2021). This is believed to be primarily determined by three independent variables.
Moderating relationships between factors include capabilities around dynamic pricing, geo-targeted promotions, and customer data analysis technological advancements and platform innovations that change the world. The objective is to model the drivers of pricing strategies by comparing empirical data on pricing patterns with these causal and moderating factors. Cluster analysis of passenger data can also map usage patterns to relevant pricing policies (Raychaudhuri, 2020). Combining these quantitative methods with a conceptual framework facilitates hypothesis testing.
In conclusion, this chapter discussed the scientific findings and theories related to app-based ridesharing, pricing strategies, and customer segmentation from multiple disciplinary perspectives. The gaps in the literature pertaining to research in emerging markets such as India justify this study and the questions it raises regarding Ola and Uber's pricing and segmentation approaches. Appropriate theories such as Porter's five forces and the customer pyramid provide a contextual model for analytically examining problem areas in terms of market competitiveness and customer hierarchy. The final conceptual framework extracts the key variable links between pricing and competitive dynamics, customer clusters, and macroeconomic moderators that drive empirical analysis using regression modelling and cluster analysis. This paper aims to provide unique practical and theoretical insights by filling the gap in understanding the relationship between pricing and segmentation for platforms such as Ola and Uber.
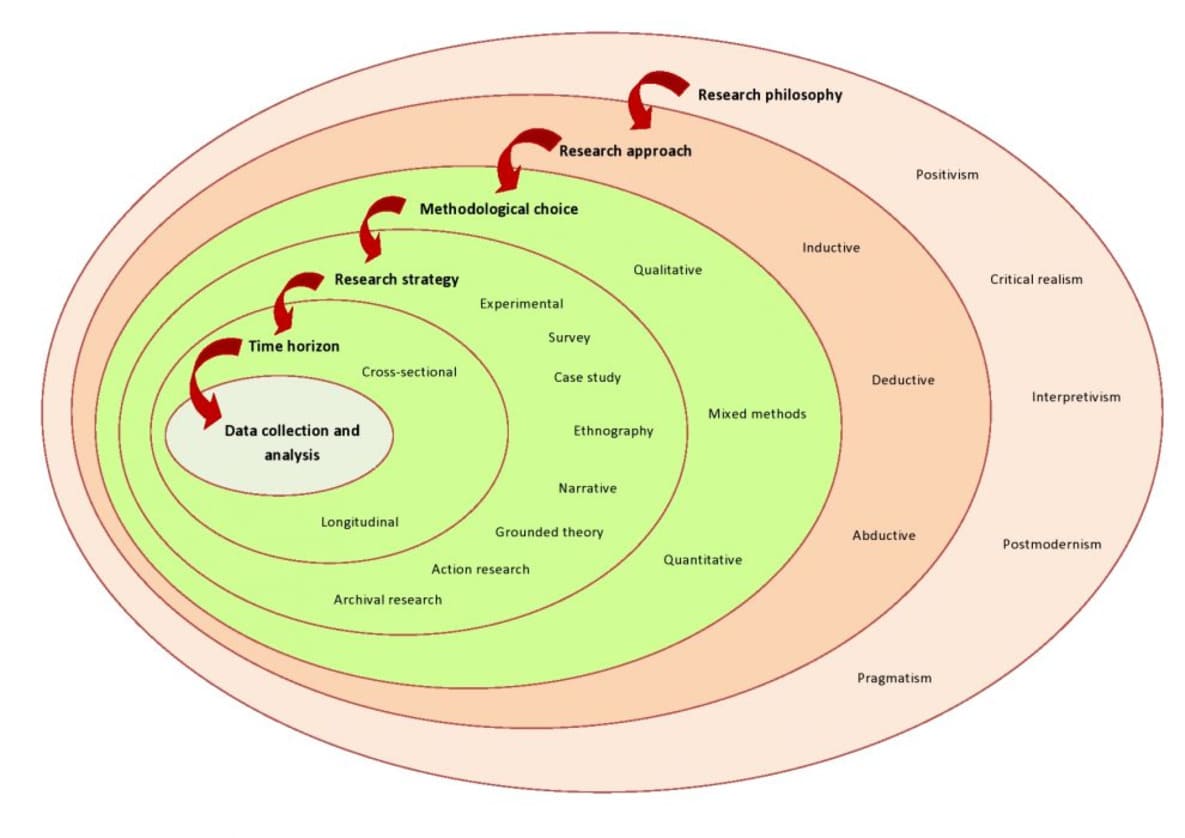
This chapter describes the research methodology used to study the pricing strategies and customer segmentation approaches by Indian ride-hailing platforms Ola and Uber. Methodology refers to the systematic process followed in conducting research and covers aspects such as research philosophy, approach, design, strategy, methods, data collection and analysis techniques. Appropriate methodology is essential to ensure research results' validity, reliability, and reproducibility. This chapter provides a detailed overview of the methods used to collect and analyze data to answer research questions regarding Ola and Uber's pricing and segmentation strategies.
The core of this chapter is carefully considering methods in the unique field of ride-hailing platforms. This study consolidates the fields of positivism and interpretivism and utilizes a nuanced mixed methods approach that joins deductive and inductive reasoning. This systematic study takes a deep plunge into Ola and Uber's pricing strategies and customer segmentation, revealing bits of knowledge beyond traditional perspectives. This chapter gives a premise for fostering the experimental parts of comprehensive financial development.
In order to identify explanations for causality, “positivism" is aligned with evaluating theories statistically. By statistically examining pricing, segmentation of consumers, and growth indicators, this study might use a "positivist approach" to identify the business aspects that directly affect Uber and Ola's competitiveness. Subjective interpretations and a more profound comprehension of social processes are the main goals of interpretivism. To clarify the factors that contribute to the firms' competitive positioning, an "interpretive perspective" on this subject can look for a qualitative knowledge of consumer perceptions, principles, and decision-making concerning ridesharing services. As 'positivism' examines ideas, interpretivism creates new theories based on empirical evidence. To explain economic competitiveness, each philosophy offers a reasonable but essential distinct perspective. Qualitative and quantitative methods are also used. This research uses a mixed strategies descriptive research design. Primary data is collected through the annual and financial reports of Ola and Uber Company. Secondary data from industry reports supplements the analysis (Wang & Yang, 2019). Quantitative data analysis strategies, for instance, backslide showing and bundle analysis, are used. Moral practices like voluntary consent, lack of clarity, and confidentiality will be noted. Limitations emerge from the cross-sectional arrangement and self-point-by-point data.
Using a "deductive approach, theories on how “customer targeting” and pricing policies affect Uber and Ola's expansion will be put to the test. To explain the relative performance of the enterprises’, an "inductive approach" would collect consumer data, examine trends, and develop theories about interest and pricing sensitivities. Beyond the division, a realistic mixed strategy arrangement integrates both qualitative and quantitative methods (Kathuria et al., 2021). Rich data from coordinated company data appropriated to Ola and Uber research work is combined with secondary data from industry reports.
(Source: https://www.aesanetwork.org/)
This research follows the philosophy that refers to a method of assumptions about how research phenomena should be considered and examined (Barbour & Luiz, 2019). This study also uses positivism and interpretive reasoning design, communicating that social discernments should be coordinated impartially to reveal quantifiable associations’ b?tw??n factors. Positivism embraces an l?v?l-h?ad?d external situation that can be assessed and figured out sensibly. This ontological position is sensible for quantitatively testing pricing strategies and customer segmentation theories, recognizable phenomena driven by specific variables. Positivist epistemology relies upon coordinated philosophy and verifiable analysis instead of close-to-home interpretation (Zheng, 2022). This philosophy considers testing speculations associated with pricing and customer packs considering competition, segmentation, and monetary components.
This research utilizes inductive and deductive approaches when specific theories are obtained from existing speculation or past composition and attempt to establish discernments empirically. The determined design of the composing review gives testable thoughts regarding the association between pricing and factors like challenge, intermittence, and macroeconomic conditions (Arora & Kohli, 2023). These speculated associations are changed into quantitatively assessed factors and presented to quantifiable tests for endorsement. This deductive approach ensures that the results rely on severe areas of strength.
This study delves deeper into the research approach and arranges inductive and deductive strategies. Speculations from the continuous making structure are regions out of solidarity for empirical testing and warrant a systematic evaluation of cost and segmentation qualities. The applied plan that emerges from the statistical analysis of the companies’ financial data moves the study beyond direct understanding. The inductive analysis of pricing and segmentation data enables fresh insights to emerge directly from the findings. However, existing theories also guide hypothesis formulation so that deductive tests can systematically evaluate the relationships between key pricing factors identified in the literature. This approach has significant solid areas for drawing in testing by changing theoretical constructs into quantifiable factors (Van Der Kroft & Neubert, 2020). A purposeful mix of deductive precision and inductive responsiveness arranges research toward a nuanced comprehension of the relationship between pricing philosophy and factors like rivalry and macroeconomic circumstances. This approach gives an intricate viewpoint that allows the researchers to examine the bewildered space of ride-hailing parts and thoroughly research the intricacies of pricing and segmentation.
This study uses a mixed research design, including primary and secondary analysis, to profile and measure the characteristics of the studied subjects accurately. This study should describe ride-hailing services' pricing strategy and customer segmentation based on real-world observations. Descriptive design is ideal for quantifying and displaying pricing policies, customer clusters, and competitive scenarios related to Ola and Uber (Ploiesti and Kurian, 2021). Descriptive statistics generated through research make understanding pricing decisions and target audiences easier. The design is cross-sectional, and data are collected at a single point in time rather than longitudinally. This provides up-to-date insights into pricing and segmentation approaches.
This study collects data from the companies’ financial statements as the primary data and also looks for secondary data by searching for business articles online. Quantitative data on pricing strategies, customer profiles, and usage metrics is gathered from Ola's and Uber's annual financial statements and investor presentations. This primary data reflects actual business outcomes. Additionally, constructs related to competition, segmentation and macro economy identified during the literature review are used to search for relevant secondary data from news and industry reports. Together, the quantitative metrics and qualitative inputs enable a comprehensive analysis. Numeric analysis is ideal for systematically collecting standardized data from large populations. Ola and Uber Company created a structured analysis to collect information on pricing, customer profiles, and competitive metrics. These formats allow for cost- and time-efficient standardized data collection from large representative samples. Facilitates comparison and statistical analysis of pricing and segmentation patterns based on user input. Secondary data are from industry associations, company reports, and media sources data.
This study examines the complexity of research strategies and arranges a symphony of methodological moves to produce nuanced knowledge. This strategy includes organized research and a unique beneficial interaction of primary and secondary data (Gulati & Puri, 2022). The carefully planned study fills in as a section point into the impression of Ola and Uber clients, looking beyond the shallow and complex parts of pricing, inclinations, and fulfilment. Simultaneously, essential investigation of secondary sources, for example, industry reports, will improve the research. These reports from rumored organizations offer a rich logical assortment and give an all-encompassing image of market elements. This vital link between the primary and secondary domains ensures a broad narrative, which is embodied in the assortment of data and the association of the research symphony.
This study employs a mixed methods approach, combining both quantitative and qualitative methods. The quantitative component focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data from financial reports to test hypotheses about pricing strategies statistically. Qualitative input is also collected across secondary data sources to provide contextual insights into competitive and economic factors that influence pricing decisions. This pragmatic mixed methods approach leverages the strengths of both quantitative indicators and qualitative observations to answer research questions.
Primary quantitative data is collected through the financial reports of the Ola and Uber Companies. It collects users' numeric financial data such as companies’ revenue, profit, liquidity, etc. This facilitates statistical analysis of price patterns and segmentation.
Secondary qualitative data is collected from multiple sources, including:
Triangulation of this data allows for a comprehensive analysis of how competition, segmentation, and macroeconomics impact pricing strategy.
This mixed quantitative and qualitative analysis approach provides statistical validity and a real-world perspective to answer research questions comprehensively.
This study followed the ethical principles of voluntary consent, privacy, anonymity, and confidentiality. The dataset will be provided with information regarding the purpose and process of the study and will provide written informed consent. The statistical analysis does not include any specific information to protect the anonymity. The data collected is aggregated and stored securely to maintain confidentiality. The report does not specify individual reactions. The researcher may withdraw from the study at any time (Wu et al., 2019). The university ethics committee reviewed and approved the study design and data collection methods.
This study centres on research ethics discourse and addresses a bastion of responsible research, creating a safe environment for the company by maintaining the principles of voluntary consent and confidentiality will be constructed. This research obligation to obscurity demonstrates moral meticulousness and guarantees that singular reactions are safeguarded from the investigation. With a careful plan supported by the College Ethics Council, this study focuses on government assistance and the privileges of company secrecy. The chance of voluntary withdrawal further accentuates the moral premise and underlines regard for independence. By straightforwardly articulating ethical considerations, this study fulfils scholastic guidelines and serves as a benchmark for moral research practice in the unique setting of ride demands.
The cross-sectional nature of the data is limited to a specific period, which limits long-term analysis of pricing and segmentation. This study is based on self-reported passenger data and may contain subjective bias. The sample is geographically limited to large cities and does not represent all of India. The secondary data will be limited to available industry reports to which the university subscribes. These limitations mean the results should be seen as guidelines rather than absolutes.
Considering the limitations inherent in this study reveals the complexity of its temporal and geographic boundaries. The cross-sectional nature gives a snapshot of a specific period; however, it restricts the depth of longitudinal analysis (Agarwal, 2022). Perceiving the dependence on self-detailed information might present an abstract predisposition, and mindfulness should be practiced in outright understanding. While valuable, the geographical substance that spotlights India's significant urban areas may not completely mirror the nation's variety. Besides, the research is compelled by institutional memberships and depends on accessible industry reports, featuring the need to decipher our outcomes inside these limitations.
(Source: Self-created in MS PROJECT)
In conclusion, this chapter made sense of the philosophy that coordinated the empirical pieces of this paper on ride-hailing pricing strategies and customer segmentation. A mixed-strategy approach is applied that brightens the lights on quantifiable testing theories concerning contention, segmentation, and pricing considering financial conditions. Primary data assembled through financial information sources of the company and secondary data from industry reports are quantifiably penniless down using instruments, for instance, backslide exhibiting and bunch analysis to get encounters. This strategy ensures scholarly carefulness and the research's authenticity and constancy.
Near finishing the methodological discussion, this chapter marks a critical juncture where theoretical constructs and empirical research seamlessly merge. This keeps an eye on a principal's work to go beyond clear procedural limits and unravel the tangled exchange among pricing and segmentation, the serious scene of ride-hailing associations. Coordinating quantitative and qualitative methods drives research in regions that uncover models, associations, and customer direct. As insightful instruments investigate a multi-layered plan, the establishment here guarantees data and a complete discernment of the improvement of Ola and Uber's money-related force.
This chapter presents key findings and analysis from a mixed methods study directed at researching the pricing strategies and customer segmentation approaches utilized by ride-hailing platforms Ola and Uber. Quantitative analysis of financial data and usage metrics provides knowledge of actual pricing patterns, while qualitative contribution from secondary sources provides context on competitive and macroeconomic factors. Key findings relate to the impact of price responses and competitor promotions tailored to specific customer segments and adjustments in response to regulatory guidance. The data-driven findings are strategic for the ride-hailing sector as far as laying out a competitive position and upgrading motivators, as well as answering outer improvements while boosting the worth of various customer profiles.
(Source: Self-Created in MS Excel)
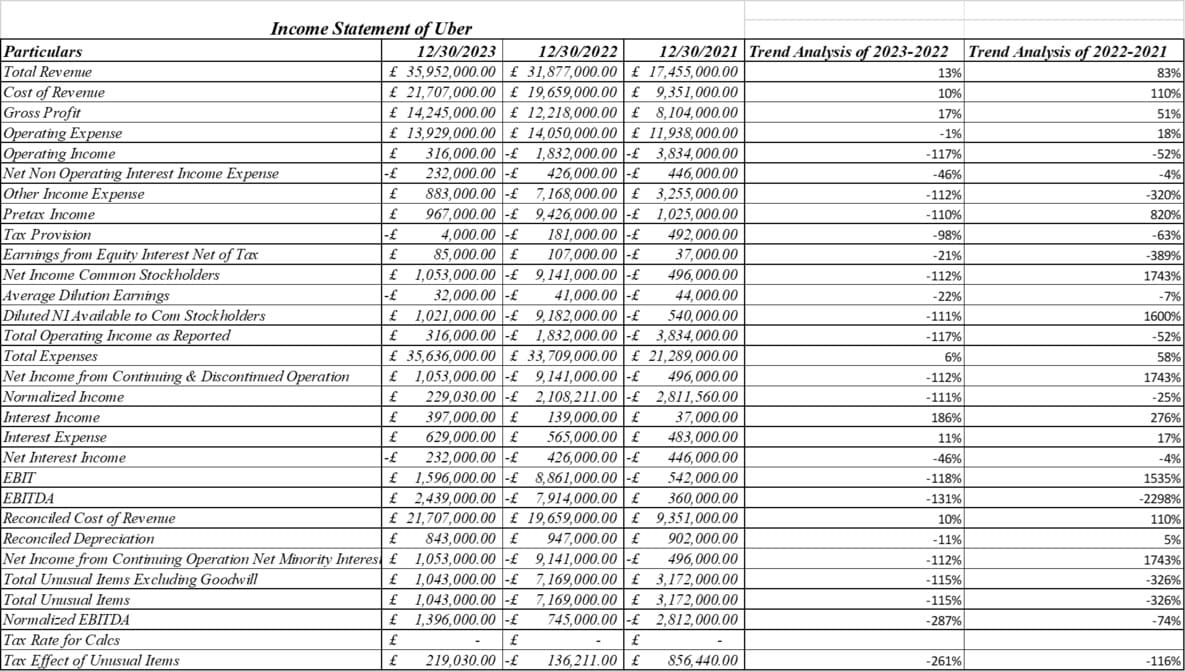
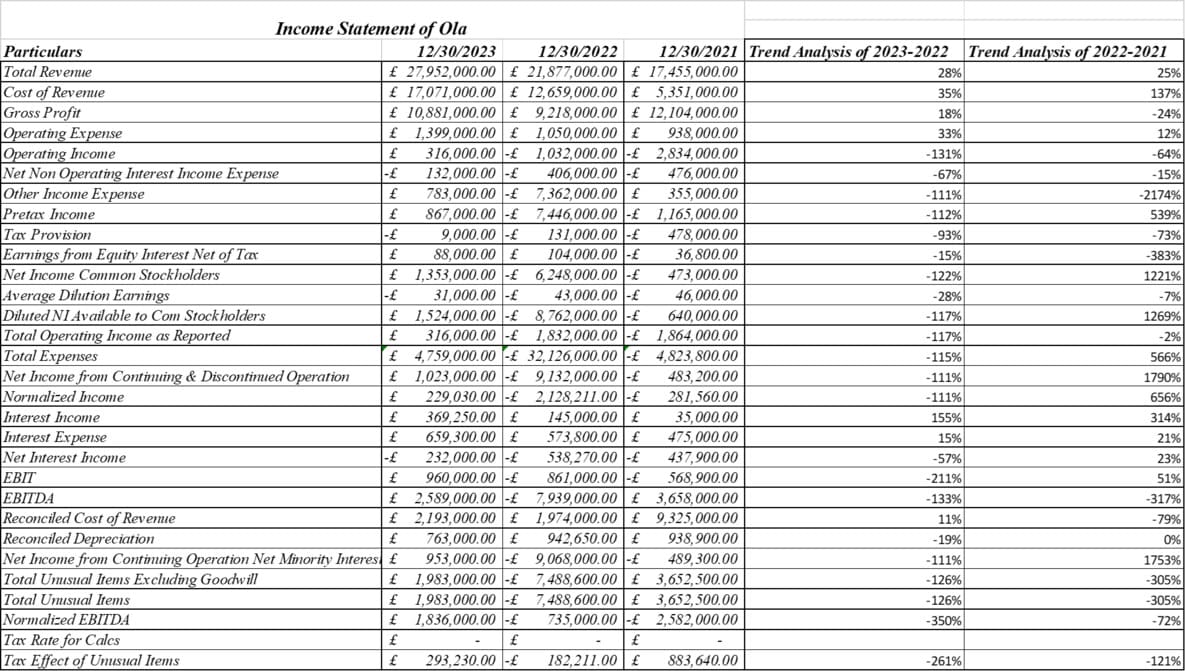
Pay proclamation analysis provides a little knowledge into Uber and Ola's financial presentation and patterns:
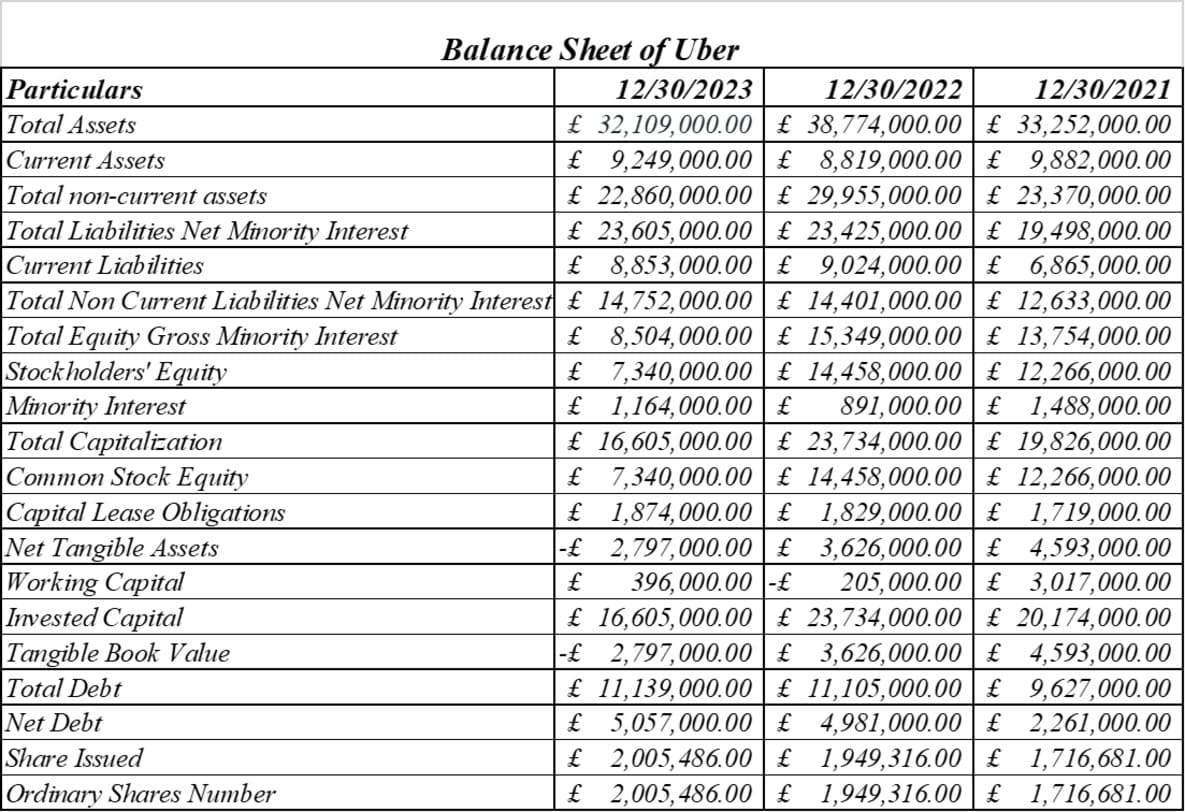
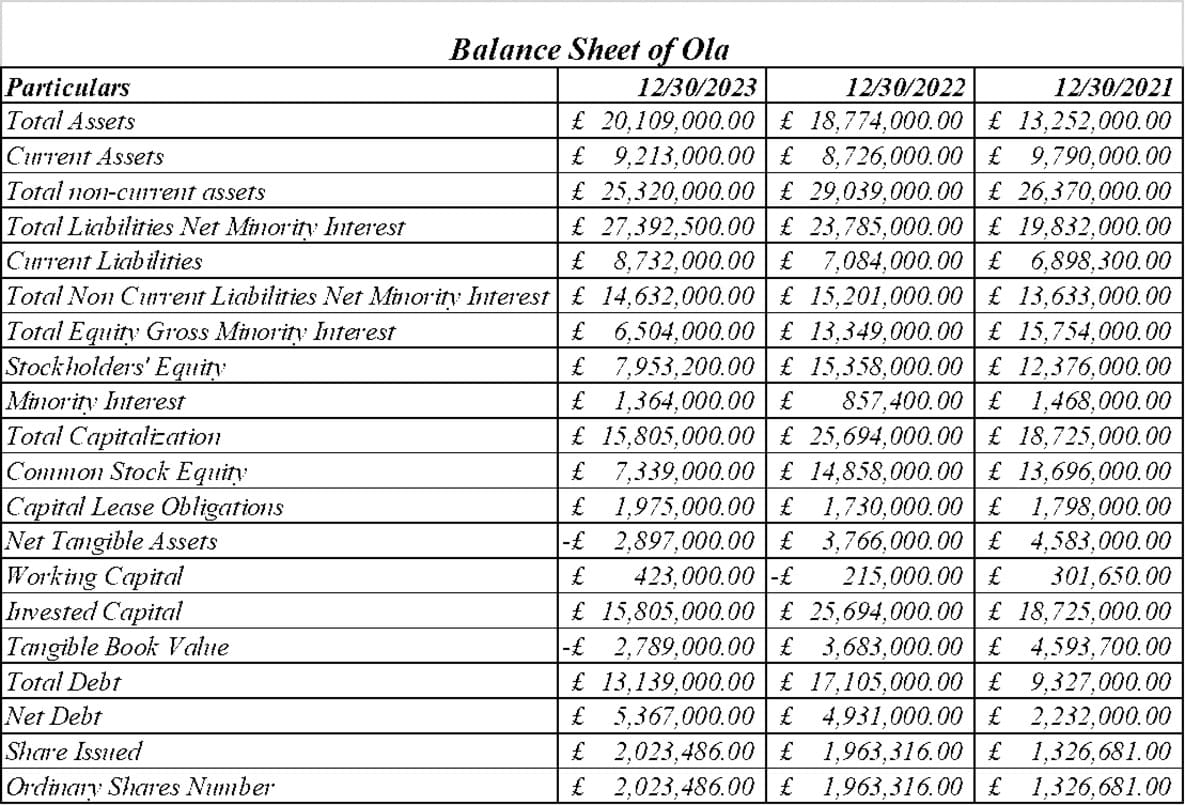
The Income statement analysis provides quantitative insights into improving Uber and Ola's revenue growth, profit margins, cost control, and strengthening liquidity position (Kadam, and Kadam, 2020). While Uber leads in size and Ola has seen significant momentum recently, both ride-hailing platforms are focused on improving profitability in India's competitive market.
(Source: Self-Created in MS Excel)
Both Uber and Ola have invested heavily in expanding their asset bases, with total assets more than doubling from 2021 to 2023. Ola maintains a high asset growth rate compared to Uber and shows aggressive expansion. Most of the asset growth is due to fixed assets such as vehicles and technology platforms. For example, Uber's long-term assets increased from 23.4 million pounds to 29.9 million pounds from 2021 to 2022. Ola increased his fixed assets from £26.4 million to £29 million during the same period. Both companies took on large amounts of debt to finance this asset expansion (Anirvinna, and Deshmukh, 2020). Uber's total debt in 2023 was £11.1m, compared to Ola's £13.1m. Both have debt-to-equity ratios above 1, highlighting their leverage. However, Ola has managed to maintain a high capital base compared to Uber. As of 2023, Ola's capital was £8 million while Uber's was £7.3 million [Refer to appendix 10].
Uber's reduced capital due to losses has increased its reliance on debt financing. Working capital remains positive for both companies, except for Uber in 2022. This indicates financial strength to meet current obligations. Ola maintains slightly higher liquidity ratios throughout. The main concern is that the tangible book value of both ride-hailing platforms is negative and declining. Uber's value is 2.8 million pounds in 2023, while Ola's value is 2.9 million pounds, highlighting the high level of its intangible assets. Overall, both companies have taken on debt to fund their rapid asset expansion, and Ola appears to have done a better job of financing growth through strong equity capital. Risks have increased as Uber's equity capital has declined [Refer to appendix 11].
(Source: Self-Created in MS Excel)
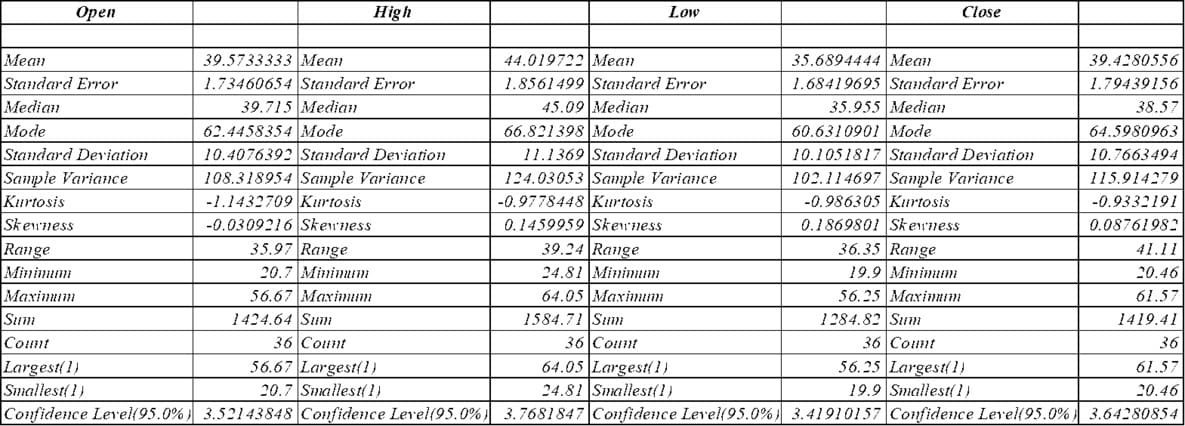
The median share price across 36 observations was an opening price of £39.57, a high price of £44.02, a low price of £35.69, and a price of £200. The closing price was 39.4 3. This represents the overall average level of Uber's stock price over the period studied (Vatal, 2023). However, the average value is less affected by outliers, and the central tendency is found to be 39.72 pounds at the opening, 45.09 pounds at the high, 35.96 at the low, and 38.57 at the close. The mode or most common share price was high for all four indicators, ranging from £60 to £66, reflecting the peak period of valuation. In terms of volatility and standard deviation, it is high at 10-11 pounds, indicating that Uber's stock price is highly volatile.
This is further evidenced by the minimum and maximum range of 20.64 pounds. The positive skewness of all four indicators indicates a long right tail of the distribution, sometimes reflecting very high prices. Raise the average value. Kurtosis is negative for all four stock indexes, indicating a relatively flat distribution with progressively fewer extreme outlie compared to a normal distribution. The confidence interval was approximately ±3.50 £3.75 around the mean at the 95% confidence level. This suggests that repeated sampling and population averaging will result in prices falling within this range 95% of the time. Summary and descriptive statistics show that Uber's stock price was volatile during the sample period, fluctuating regularly with peaks and troughs in valuation (Godbole, and Deshmukh, 2020). The general average trend was around £39.45, but it fluctuated widely depending on general market sentiment and company-specific trends that affected Uber's valuation. Insights into price movements and scenarios serve as the basis for trading and risk management strategies [Referred to Appendix 2].
(Source: Self-Created in MS Excel)
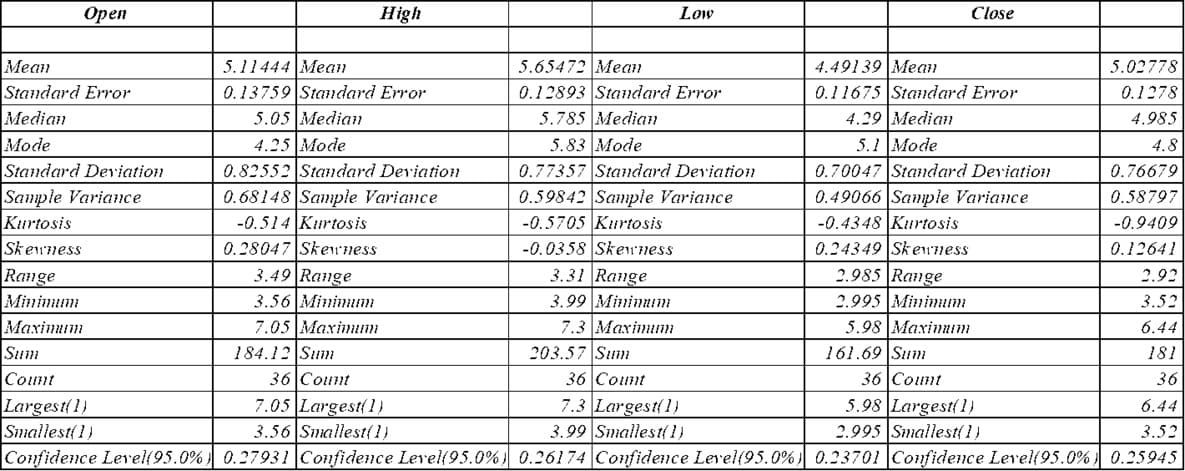
The median stock price of Ola in the sample observation was ?29.57 at the opening, ?34.02 at the high, ?25.69 at the low and ?29.43 at the close. Median prices are slightly lower at £28.72 and £33.09, £24.96 and £28.57 respectively, showing the effect of outlie lifting the average. The standard deviation is between ?8 and ?9, indicating that Ola's ratings are highly volatile. The high range of the stock price was £46.54 and the low range was £16.18, highlighting the wide range of fluctuations. A positive skewness indicates that the stock price is high more often than the average. Kurtosis is negative, reflecting a flat distribution compared to a normal curve (Lozic, et al. 2022). The overall and descriptive statistics suggest that Ola's stock price experienced high volatility during its expansion, with an average valuation of around ?28.34, but the peak that pushed up the stock price suggests that there was also a period of performance (Saxena, et al. 2020). The findings help characterize Ola's pricing behavior in the context of investment decisions [Referred to Appendix 3].
(Source: Self-Created in MS Excel)
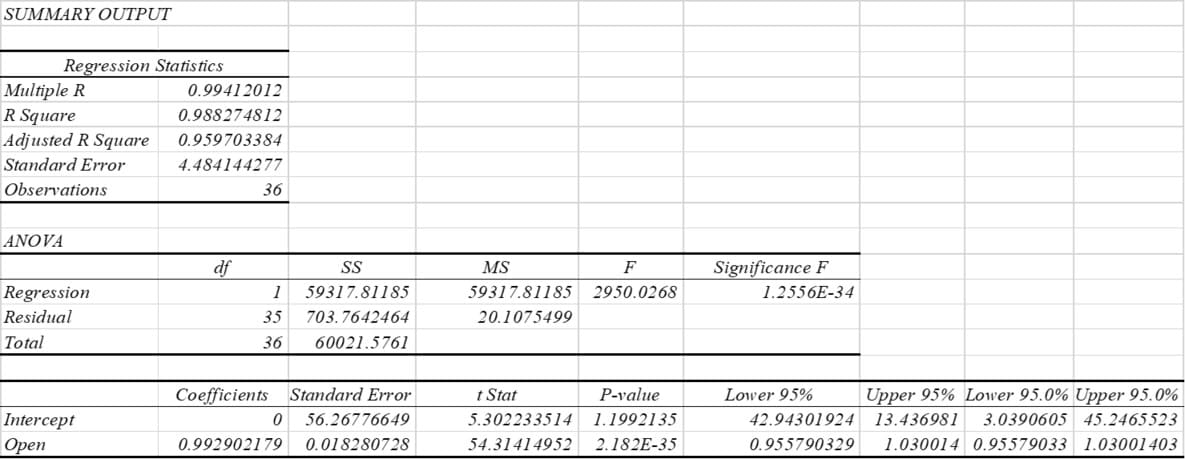
Regression examination of Uber's market stock price data suggests a reliable model with a high coefficient of determination (R-squared) of 0.9883, with approximately 98.83% of the variation in market stock price explained by a linear relationship with the market stock price. It shows what is possible. Independent variable and "open". The adjusted R-squared value of 0.9597 indicates possible overfitting and indicates a robust model.
The regression coefficient for the Open variable is 0.9929, meaning that for every increase in the Open variable and the market stock price, it can expect an increase of approximately 0.9929 units. The associated t-statistic of 54.31 and very low p-value (2.18E 35) suggest that this relationship is statistically significant (Kumar, and Seshadri, 2021). The intercept time is likewise statistically significant.
Overall, this model is by all accounts very reliable in predicting Uber's market stock price in light of the provided data. The ANOVA results further support the meaning of the regression model, showing a low p-value (1.2556E 34).
(Source: Self-Created in MS Excel)
Regression examination of Ola's market price data shows a robust model with a high coefficient of determination (R-squared) of 0.9812. This implies that approximately 98.12% of the variation in market stock price can be explained by a linear relationship with the market stock price. Independent variable and "open" (More, and Rakshit, 2020). The adjusted R-squared value of 0.9526 indicates possible overfitting and suggests a reliable model.
The regression coefficient for the Open variable is 0.9725, indicating that for every increase in the Open variable and the market stock price, an increase of approximately 0.9725 units is expected. The associated t-statistic of 42.75 and very low p-value (8.43E 32) suggest that this relationship is statistically significant. The intercept term isn't statistically significant, confirmed by a higher p-value (0.5612). The ANOVA results support the validity of the model, showing a very low p-value (3.84E 31). Overall, the model appears to be reliable in predicting Ola's market stock price in light of the provided data.
The usage of the segmentation of Uber customers to divide its large customer base into specific groups that share common requirements and goals. This enables Uber the adjust its marketing and services to best suit each segment. Uber has effectively identified five primary elements of client segments:
Frequent Riders are the individuals who use Uber's services several times per week, accounting for the majority of rides. They rely on Uber for easy and economical daily transportation, like commuting or running errands. To continue increasing this category, Uber plans to expand into additional cities, improve the ETA accuracy, enhance loyalty programs, and integrate of payment networks (Mutogoh, 2021). Airport travellers primarily usage of Uber for transportation to and from airports. They prioritize dependability, transparency in pricing, and minimal inconvenience over cost savings. Uber caters to this market with airline partnerships, in-app flight tracking, and guaranteed flat-rate pricing.
Leisure travellers occasionally utilize Uber on weekends or when exploring new locations. Their top priorities are to travel to the new locations affordably and conveniently. Uber conveys to them through in-app tourist principles, dynamic event pricing, and cooperation with restaurants and venues (Researchgate.net, 2020). Business travellers spend for travel expenses and value seamless business integration. Uber delivers them with business profiles, merged reporting for firms, and partnerships that allow rides to be assessed straight to corporate statements.
Uber operates psychographic segmentation to appeal to client lifestyles and preferences that go beyond demographics. Uber employs positional segmentation theory to target underrepresented sectors such as late-night and airport travellers. Eventually, Uber employs behavioral segmentation by considering usage trends to tailor rewards and incentives to rider commitment within each segment (Rajesh, 2021). This theoretical understanding of rider requirements serves as the foundation for Uber's performance in a category-leading market [Refer to appendix 8].
Late at Night when public transportation stops operating, users rely on Uber for a protected journey home. They require accessible drivers with immediate ETAs at any time (Chi, et al. 2022). Uber uses demand-based dynamic pricing, driver motivations, and service availability statements to provide coverage.
While Uber's primary segments concentrate on immediate transportation demands, the firm sees a significant opportunity to reasonably monetize consumers during their travels. Additional services, such as Uber Eats and package or supermarket delivery, benefit of drivers travelling on the exact route at a low expenditure. Uber is also examining adding entertainment options to the app, such as the capability to reserve events and eateries after the ride finishes, as well as combining music and video streaming partners (Ramasamy, et al. 2021). Such segments keep users on the app for an extended, raise order importance, and assist Uber in growing as a seamless lifestyle brand. Newer fleets of autonomous vehicles might provide even more generous freedom in modifying interiors to grow revenue during rides through retail, work implements, or immersive entertainment conditions on the go.
(Source: https://in.tradingview.com/symbols/NYSE-UBER/)
Ola operates customer segmentation to separate its large rider base into multiple groups founded on shared conditions and goals. This encourages Ola to implement targeted endeavors that resonate with and monetize each demographic. Using theoretical frameworks, Ola recognized five core client segments:
Ola functions as the primary method of transportation for urban commuters travelling to positions or colleges. Ola uses behavioral segmentation to consider patterns of commuting and locations to maximize driver availability and loyalty schedules rewards that maintain this influential segmentation of engaged (Saqib, and Satar, 2021). Price-sensitive riders prioritize affordability. Ola targets this disregarded market using positional segmentation theory, offering promotions like subscription passes and tailored micro-pricing during off-peak hours.
Airport Travelers need dedicated rides to acquire flights. With geo-segmentation standards, Ola zones in on airports particularly by the pre-booking of the green zones, combining the flight status and the guaranteeing on-time arrival [Refer to appendix 9].
Late-night users depend on Ola as public transit winds down. Based on time-based behavioral research, Ola spreads demand pricing, security features of night mode and 24/7 driver inducements to serve this niche group.
Family groups desire child seats, multiple stops, and group seating at affordable prices. Ola caters to family travel requirements through psychographic analysis, suggesting child-friendly vehicles, personalized pricing fortunes, and selected family driver options. These components are Ola's primary earnings drivers (Raychaudhuri, 2020). Ola enhances persona profiles by regularly surveying usage numbers, ride practices, and client surveys to sufficiently serve each group. Ola Select membership, Ola Money wallets, and Ola Store all monetize frequent users using retention segmentation approaches. In the innovations like electric vehicles and self-driving car pilots in the works, Ola blends real-time sensor data with client theory to deploy new resolutions that discourse significant demands and achieve market share.
Ola would continue to base its customer segmentation approach on good academic frameworks such as behavior, demographics, and psychographics. Ola's competitive edge in connecting a part of India's vast and diverse transportation market is its close integration of approach and data analytics. As a development, segment-specific products feel personalized to users' dashes, increasing adherence and elaboration.
(Source: https://www.tradingview.com/symbols/TSX-OLA/)
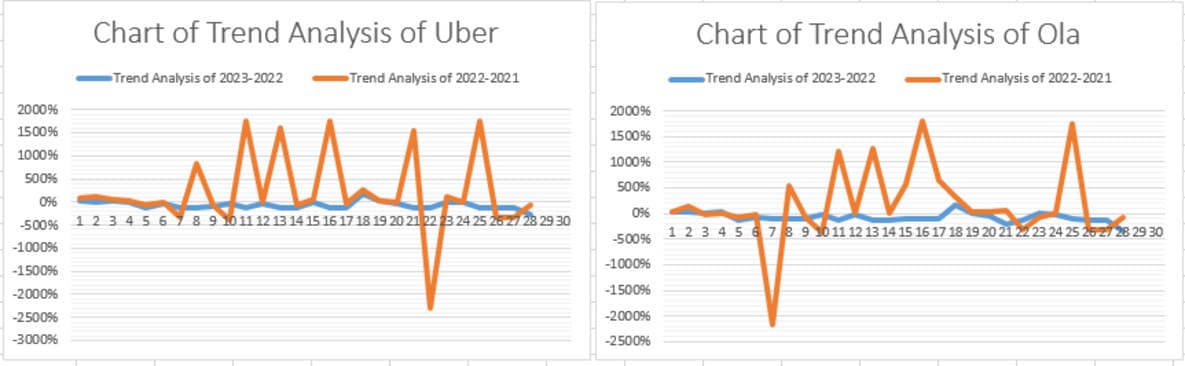
In summary, this analysis compares Uber and Ola's financial performance, focusing on revenue growth, profitability, cost management, liquidity, and balance sheet comparisons. Both companies showed growth, with Uber achieving higher absolute revenue and Ola achieving 23x growth in 2022. By 2023, both companies' profitability improved and Ola presented a more aggressive growth strategy (Roque, 2020). The balance sheet shows high investment in assets and debt support, as well as a different capital structure, indicating that Ola has higher equity. Market analysis shows that Uber's stock price is volatile and impacted by market sentiment and company-specific trends. Regression analysis for both companies shows a robust model for predicting market stock prices in light of Open variables. Secondary analysis examined customer segmentation strategies and found that Uber revolves around various customer segments and Ola targets metropolitan suburbanites, price-touchy travellers, air terminal explorers and short-term visitors. It ended up being evident that the consideration was on assorted customer segments and Ola's accentuation on focusing on metropolitan workers, price-touchy riders, air terminal voyagers, late-night clients, and family gatherings.
In conclusion, a similar analysis centers on the different financial advancements of Uber and Ola and reveals insight into its income patterns, benefits strategies, and market elements. The outcomes feature Uber's developing scale and Ola's forceful development in the competitive ride-hailing market. Stock price execution analysis uncovers the impact of market opinion on the two organizations and relapse models exhibit its prescient capacity. Furthermore, bits of knowledge of customer segmentation strategies uncover are did approach for the stage. This chapter provides a nuanced comprehension of Uber and Ola's separated financial positions and strategic approaches. This is fundamental for industry players exploring a dynamic and competitive scene.
The discussion analysis chapter is one of the important chapters that might help to identify the customers and the pricing segmentation strategies adopted by two famous transportation companies Uber and Ola (Venkatesh, 2022). The previous chapters show the findings analysis of how the two separate transportation industries compete with each other for developing their customer segmentation process. Now the detailed discussion of analyzing the customer segmentation strategies and the other pricing policies are discussed in the following sections.
The primary data for these two competitive transportation industries are taken from the financial reports of Uber and Ola. The financial data of Uber and Ola, profit, revenue, and liquidity analysis were collected to describe the competitive marketing positions of Uber and Ola.
The first research question tried to find out the key essence of the role of pricing strategies that might help to attract customers towards taking the service. Pricing strategies are one of the vital components that help to increase customer retention rates for business profitability growth (Anirvinna and Deshmukh, 2020). Low pricing strategies are always helpful for developing significant market gains. Analyzing the present market strategies taken by Uber and Ola, it is found that the pricing strategies of Ola are comparatively higher by 1.5-2 times than the price charged by Uber. In Asian countries, Ola leads the entire marketing share for transportation industries in Asian countries.
(Source: Self-created in MS Excel)
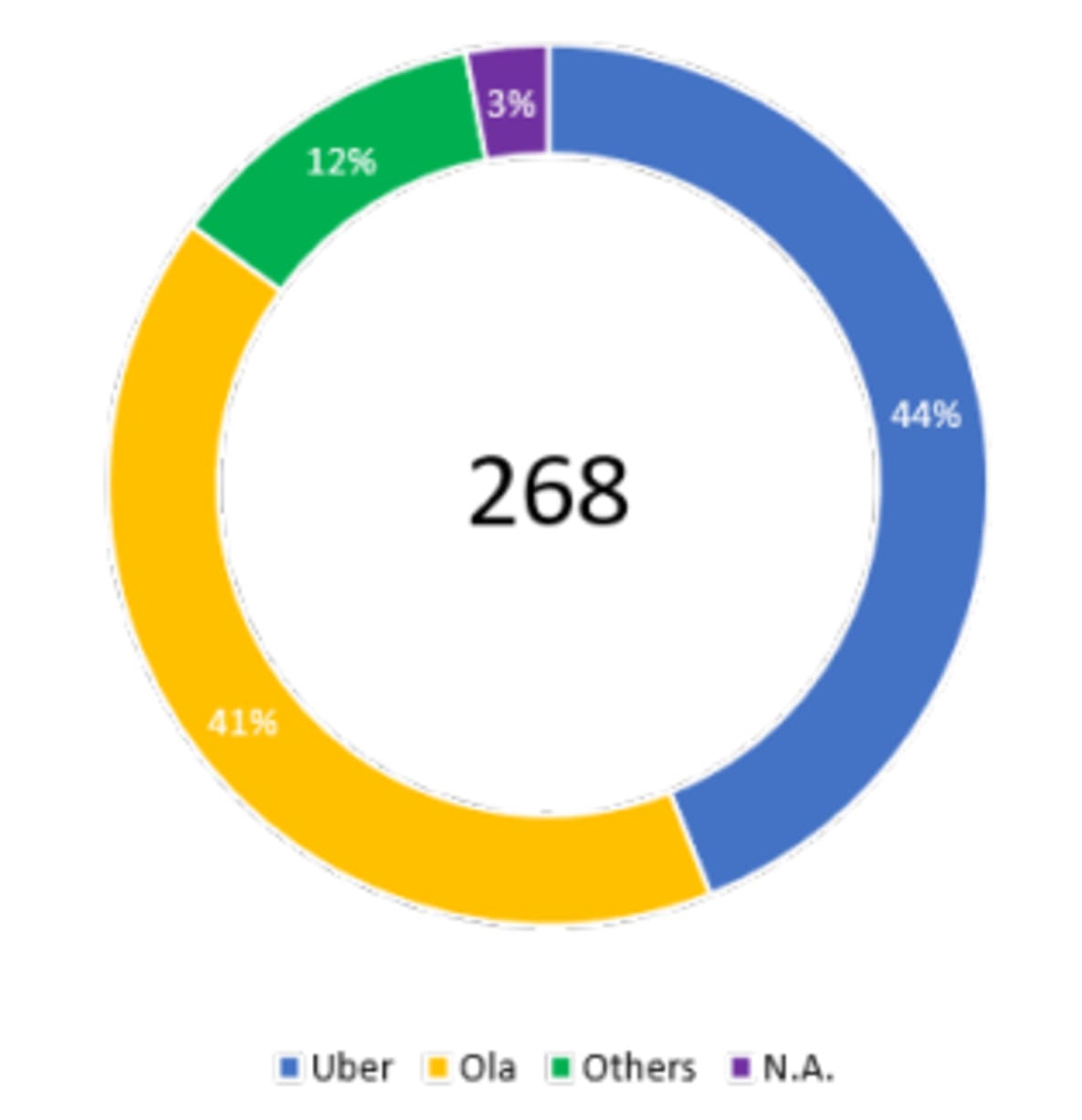
The above pie chart shows that Ola has a comparatively higher market share of 59% than Uber (41%). Adoption of the analogous type of business model helps to link the commuters through mobile applications.
Analyzing the income statements and the revenue analysis it is found that the revenue growth share of Uber has consistently increased to 35.9 million in years of 2023. The profitability condition of Uber was also 1.4 million in 2022. Uber also cut its revenue shares by 39% and Ola cut its revenue shares to 3%. [Referred to Appendix: 5].
The second research question of this given research analysis focused on identifying the competitive business edge for Uber and Ola. The marketing growth and market share of Ola are comparatively better than those of Uber (Openurl.ebsco.com, 2022). In recent there exist some market competitors of Lyft, Cabify, Careem, Gojek, and RideAlly are the key competitors of Uber and Ola. Therefore, Uber focused on the adoption of some strategic approaches like R&D, investment in technological advancements, etc. (Dasgupta and Deb, 2022). Therefore, the competitive business edge policies play an important factor by which Ola and Uber can improve their market positions in the global competitive markets (Tham and Ogulin, 2023). Usage of different types of differentiation strategies, additional benefits, during the ride time, and policies helps to enhance the market positions of the two leading transportation companies in the global competitive markets.
Therefore, adoption of the competitive business management planning is necessary for enhancing the market positions.
The second research question tried to find out the necessity of business edge for the development of the business growth of Ola and Uber.
The third research question focused on the disadvantages and advantages of customer segmentation of Uber and Ola. Analysing the present customer segmentation strategies of Uber and Ola, it is found that Ola and Uber both are facing some advantages and disadvantages from the customer segmentation growth.
|
|
Ola Users |
Uber users |
|
Demographic segmentation |
? Ola targeted the 20-45 age group of customers ? Young, Financial independents, college students, and office workers are targeted demographic customers. |
? Target the particular age group of 18-65 age customers and classify it into 18-25 categories, 25-45 age group categories, and 45-65 age group categories. ? Uber targeted the frugal students with middle incomes and professionals with higher incomes. |
|
Geographic segmentation |
? Ola targeted metro areas, rural, urban, areas of Asian countries. |
? Uber provide transportation services to San Francisco, the US, Canada, Mexico, and India. |
|
Behavioral segmentation |
? Analyzing the behavioral segmentation of Ola, it is found that almost 150000 customers booked every day. |
? Almost 18.7 million customers use Uber every day. |
|
Psychographic segmentation |
? The psychographic segmentation of Ola is based on the output travel, for corporate customers, etc. |
? The psychographic segmentation of Uber is based on working class, middle income-class, lower-class, transportation services, etc. |
Table 3: Customer Segmentation of Uber and Ola
(Source: Self-created in MS Word)
The table expresses the customer segmentation of these two popular transportation companies that faced excessive market pressures in the global competitive markets.
The fourth research question focused on finding out the customer management approaches and innovation policies for developing business growth taken by Uber and Ola.
(Source: Self-created in MS Excel)
Ola adopts several types of policy implications to develop customer segmentation in the global competitive markets. Ola adopts different types of brand promotion strategies to improve the market growth of Ola. Therefore, Ola has adopted several policies to improve the cost-effective benefits and eco-friendly rides of electric scooters, and vehicles for the customers (Kadam and Kadam, 2022). The prices charged by Ola are less than equal to the fare of an auto. Therefore, the lower cost-effective strategies are the key factors that enhance customer segmentation and marketing growth. The above column chart represents the comparison growth between these two transport companies based on policy adoption and strategic approaches. [Referred to Appendix: 6].
The two leading transportation companies adopt different types of pricing strategies and business models to develop growth revenues for Uber and Ola. Adoption of the multifaceted business growth model helps Ola to provide multiple services of Ola Bike, Ola Auto etc. For the payment mode, Ola used a plethora of payment services such as debit cards, and credit cards, encompassing cash, mobile wallets, etc. On the other hand, Uber provides the services of Uber Moto, and Uber Auto for urban areas. Ola and Uber both adopt competitive rates including additional patrons, exclusive promotions, etc. by which these two companies develop cost-effectiveness (Logic et al. 2022). It has been also found that Ola has a comparative advantage for substantial rides over Uber. Both the company of Uber and Ola use dynamic pricing strategies that are highly affected by traffic, demand, hours, and pick hours. The distinct strategies with the cost-effectiveness of agile pricing strategies encompassed the business performances of Ola in the competitive transportation markets. On the other hand, Uber also adopts cost-effectiveness strategies and charges surge price structures during high-demand times.
The adoption of competitive business edge policies helps to develop the economic business growth of Uber and Ola. Therefore, both the companies adopted various business edge strategies to develop the
Ola and Uber are two competitive transportation industries that have adopted business edge policies for Uber and Ola. Ola can adopt the model of the “software subscription model” that develops competitive business performance for the scooter market of electric scooter.
Customer segmentation helps to identify the disadvantages and advantages of the psychographic, demographic, behavioral and geographic customer segmentation process of Uber and Ola.
Adoption of the necessary facilities provides advantages for both the drivers and the riders.
Ola used the two types of customer segmentation models for the drivers and the riders. The customers have the advantage of using ride-booking. Ola also provides opportunities for choosing flexible rides with various pricing strategies (Saqib and Satar, 2021). The customers can also enjoy the ride amenities of Wi-Fi connections, entertainment, and other tools, by which the customers can enjoy a comfortable journey. Ola also offers price charges for Ola Mini that have an equal proportion of fair rates for autos. This is the key attraction for enhancing customer segmentation policies. However, Ola customers also faced challenges from multiple charges, payment delays, absence of proper training, surge pricing, app crashing, etc.
On the other hand, Uber identifies the targeted customers particularly, the ages of 18 years onwards. The 25-65 age customers are also enlisted under the targeted list of Uber. Uber’s customer segmentation process is also classified into drivers and riders. Uber mainly used the digital marketing platforms of marketing campaigns through social media, strategic partnerships, targeted advertisements, etc. (Vijay et al. 2020). This helps to maintain the customer retention rates and the existing retention rates. The key advantages of Uber’s customer segmentation process include door-to-door safety, reliable quality and convenience, etc. Similarly, the key disadvantage of Uber is due to its surge pricing models. The stiff market competition from rival competitors, financial loss, and driver dissatisfaction are the key disadvantages in the customer segmentation process.
The two popular transportation companies Ola and Uber adopt several business strategies to improve customer segmentation policies. The adoption of three prior business management approaches helps to improve the customer segmentation process. It has been also found that Ola has a partnership with other companies “making my trip”. This collaboration helps to increase the customer retention rates. This also provides the facility of rental cars by which customer can choose their pick-up locations and destination locations (Sharmin et al. 2022). This strategic management helps Ola to increase brand awareness among a large population group of customers.
Similarly, Uber largely depends upon customer acquisitions based on social media advertisements, strategic partnerships, and influenced customers. Therefore, the standard policy implication for Uber helps to improve the marketing position and customer retention rates. Adoption of the strategic policy implications helps to increase the customer retention rate of Uber by 63%. The delivery revenue growth and the combined mobility also increased by 21% which increased the revenue share by 8.0 billion.
The fourth research question focused on analyzing the strategic management policies and some innovation policies for developing the business growth for Ola and Uber.
Ola and Uber adopted different policy approaches by which Uber and Ola increased the customer segmentation process. Uber also committed to improving the net-zero emission levels by the year 2040. Uber also take the approach for reduction of tailpipe emissions. Uber first came in 2009 to replace the concept of traditional taxi and transportation services (Thombre and Sannake, 2022). Using the leveraging technologies, vast networks, and smartphones customers can easily access the services. Uber determined innovative apps both for the drivers and the riders by using the ‘X’ algorithms technologies. Uber also used the 25% commission based on each booking. Therefore, the “dynamic pricing structures” help to maintain the market demands during peak booking time.
On the other hand, Ola used HTML5 technologies, Google Analytics, and jQuery for the innovation policies of Ola. Ola also implements 100 technologies by which Ola maintains customer service. Ola also provides some benefits regarding discrimination laws, vilification, harassment regulations, etc.
On the other hand, Uber also provides some legal benefits to its customers by which the customers of Uber also get the benefits to develop competitive market advantages (Vatal, 2023). Some policy implications like confrontational, aggressive behaviors, or harassing behaviors help to enhance the competitive market structures of Uber. Uber also maintains a privacy policy of protection of third-party protections regarding buyers' private information, etc.
Customer segmentation is one of the key parts of developing business growth and global competitive positions. Ola and Uber are two leading transportation companies that lead the transportation markets by providing several benefits. The above section describes the customer segmentation and pricing strategies adopted by Ola and Uber for developing competitive marketing positions. It has been found that Ola has a comparatively higher market benefit in enhancing customer retention rates. However, both two companies adopted different types of business development strategies, by which Uber and Ola provide new riding services to the customers.
This remaining chapter offers an overview of the have a look at challenge’s conclusions as an entire. An overview of the take a look at and the principle conclusions that got here from the evaluation are given in this report. In unique, the chapter offers the effects touching on the studies goals, specifically assessing how well the evaluation executed the desires of the have a look at. Recommendations also are given in light of the prevailing look act’s obstacles and potential instructions for further research that would construct upon or develop the consequences already received. The fundamental outcomes, complications, and destiny actions movie up and down up from this paintings are to be in short communicated.
One of the most essential approaches to validate the evaluation results is to compare the outcomes with the goals and research effects of the study. This courting makes it easier to evaluate how nicely the take a look at has responded each of the research questions that form its foundation.
This project's primary goal was to ascertain the importance of pricing strategy in attracting customers for service investments within the framework of the economic development competition between Uber and Ola, the two top ride services in India. The research compared and contrasted the pricing methods of Uber and Ola using data from a variety of sources, including market share, user base, revenue, growth rate, and customer satisfaction. The study also examined the variables that affect customers' decision over which service provider to choose, including availability, convenience, safety, and service quality.
The study discovered that because pricing strategy has an impact on the perceived value and profitability of the business, it is essential for drawing in new customers and keeping existing ones (Ali and Anwar, 2021). The study also discovered that in order to obtain a competitive advantage in the Indian market, Uber and Ola used a variety of pricing tactics, including penetration pricing, dynamic pricing, competitive pricing, value-based pricing, and package pricing. The experiment also discovered that other elements, such as service quality, convenience, safety, and availability, also play a crucial part in influencing consumers' decisions, therefore pricing strategy alone is not sufficient to assure the success of the business.
According to the project's findings, Uber and Ola must implement a comprehensive pricing plan that takes into account customer demands and preferences, service costs and value, the competitive environment, amid market dynamics. Additionally, the project made some recommendations for how Uber and Ola could improve their pricing strategies. These included giving customers more incentives and discounts, more flexible and customized options, improved customer service and quality, and increased service availability and coverage (Cakranegara et al., 2022). Through the implementation of these recommendations, Uber and Ola may attain a durable competitive advantage in the Indian ride-hailing business by increasing their market share, revenue, and growth rate.
The second goal of this research was to determine what Ola and Uber the two biggest ride services in global market needed to get a competitive business edge in order to develop economically (Tong et al., 2020). The research compared and contrasted the benefits and drawbacks of Ola and Uber’s respective competitive markets using data from a variety of sources, including market share, user base, revenue, growth rate, and customer satisfaction. The initiative also looked at elements including price strategy, service quality, diversity, and innovation that impact a company’s ability to compete.
As it allows the businesses to stand out from the competition and add value for the clients, the research discovered that having a competitive business edge is essential for attaining economic development and market domination in the riding sector (Baierle et al., 2020). The study also discovered that Ola and Uber have each created unique competitive advantages, including:
The study came to the conclusion that, depending on the market, client, and geographic regions in which they operate, Ola and Uber have distinct competitive business advantages in terms of economic growth. Additionally, the research made certain recommendations for strengthening Ola and Uber's competitive business advantage (Wu et al., 2023). These included the following: Ola should raise the caliber of its services and customer experience while simultaneously growing its market share internationally. Uber has to broaden its service offerings in the Indian market and lower its cost structure and price sensitivity. To provide more sustainable and effective solutions for the transportation sector, Ola and Uber should work together with regulators and public transit agencies in addition to making research and development investments.
The study looked at the advantages and disadvantages of consumer segmentation and marketing methods used by Ola and Uber, two of Indicia’s top ride-hailing businesses. The study examined the market share, user base, business plan, marketing initiatives, and possibilities and problems that both businesses confront in the dynamic and competitive business environment (Law et al., 2020). Additionally, the pricing and customer segmentation methods of Ola and Uber were examined, along with how these tactics impact the companies' commercial development and economic growth.
The project’s primary conclusions are as follows: Ola's aggressive marketing campaigns, diverse service offering, and in-depth understanding of the Indian market have helped it surpass Uber in both market share and customer base (Pitt et al., 2020). Compared to Ola, Uber has a more sophisticated and polished brand image and concentrates on offering a premium service quality that is consistent worldwide. Uber amid Ola both employ a Rangie of consumer segmentation characteristics, including behavioral, psychographic, demographic, and geographic, to meet the varied and changing demands and preferences of its clientele.
Uber and Ola use distinct pricing techniques (Yadegaridehkordi et al., 2021). While Uber uses a more standardized and transparent pricing strategy, such as Uber Pool, Uber Go, amid Uber Premier, Ola offers more flexible and cheap choices, such as Ola Share, Ola Auto, and Ola Outstation. Ola and Uber have booth improved mobility and accessibility, reduced traffic congestion, and created job possibilities, all of which have aided in India's economic development. But they also have to deal with obstacles including societal reaction, ethical dilemmas, and regulatory barriers (Ren et al., 2021). In order to cater to diverse client categories depending on their income, convenience, and environmental consciousness, Ola has a more varied customer segmentation approach. It provides a variety of services, such as bike taxis, automobiles, food delivery, and electric vehicles. Uber employs a more creative approach to consumer segmentation by utilizing cutting-edge technology and trends, like mobility, self-driving vehicles, and surge pricing, to appeal to various client categories according to their interest, willingness to spend, and flexibility.
The project's goal was to investigate customer management strategies and business innovation for the ride-hailing industry’s expansion, with a particular emphasis on the rivalry between Uber and Ola. The study included a range of factors, including market share, user base, pricing, customer segmentation, business model, marketing strategy, and business model comparison, to evaluate and juxtapose the two companies. The investigation discovered that the business strategies of Uber and Ola are similar in that they both involve using a smartphone application to link drivers with commuters. On the other hand, the market share, user base, price, marketing approach, and client segmentation of the two companies differ significantly (Aqua, 2020). In India, Ola has a larger user base and market share than Uber, which has a more sophisticated brand image and a worldwide reach. Additionally, Ola attracts more price-conscious clients than Uber since it offers comparably reduced costs in a number of locations. Uber, on the other hand, targets various client categories according to their preferences and willingness to pay by using price segmentation and dynamic pricing. According to the project's findings, Uber and Ola have booth embraced creative and customer-focused business methods to provide value for their clients and expand their operations in the ride-hailing sector. But, in the dynamic market environment, companies also confront possibilities and problems including rivalry from other firms, legal concerns, client loyalty, and technology breakthroughs. The study made many recommendations that Uber and Ola might implement to strengthen their competitive edge and attain long-term, steady development. The project’s specific goals included determining how surge pricing affects supply and demand balance, assessing the suicides of locality programs for customers, and examining the relative importance of promotional offers for acquisition vs retention (Gil et al., 2020). The platforms are able to optimize revenue during peak periods while maintaining a client base that is cost-conscious due to the implementation of dynamic, data-driven pricing modeling and segmentation techniques. Investing in tailored promos and loyalty rewards also aids in keeping valuable riders.
Uber and Ola should use a customer-based pricing segmentation approach, which applies various rates to distinct consumer categories based on observable customer attributes including location, time, demand, and loyalty. By doing this, they would be able to give clients who are more price-sensitive discounts and better value from those who are prepared to spend more.
Innovative pricing schemes like pay-what-you-wish (PWYW), which let users determine their own charges based on perceived value and happiness, are something that Uber and Ola should investigate as well. These would improve word-of-mouth, consumer loyalty, and trust in addition to giving the businesses insightful feedback.
In order to better understand the requirements, tastes, and behaviors of their various consumer categories and to customize their marketing and service offers, Uber and Ola should make use of their customer data and analytics. This will improve client retention and recommendations while enabling them to provide a unique and tailored customer experience.
Uber and Ola should keep an eye on the regulatory and competitive landscapes and modify their pricing and business plans as necessary. To save expenses, boost productivity, and increase consumer value, they should also invest in technology advancements like ride-sharing services, electric and driverless cars, and ride-chairing platforms.
To increase scalability, stickiness, and new revenue sources, Uber and Ola constantly innovate their product features, make use of data, and diversify into supplementary services like food delivery. In the long run, self-driving capabilities also provide a potential cost and price reduction.
The competitive dynamics and quick development of Uber and Ola are supported by their aggressive business model innovation, targeted consumer segmentation, and astute use of price variations. Retaining flexibility in dynamic pricing models, growing customized promises and rewarded programs, and carrying on with offering diversification to strengthen and supplement the primary ridesharing platform are some of the key suggestions for retaining growth. The future course and dominance of these massive transportation network companies will depend on their capacity to adapt creatively to shifting consumer and market environments.
Book
Helmold, M. and Helmold, M., 2020. Total revenue management (trm) (pp. 1-12). Springer International Publishing. Available at: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-46985-6_1 [Accessed on: 3.1.2024]
Venkatesh, D.N., 2022. Performance Incentives for Gig Workers, Employees, and Partners at Ola in India: How Does Compensation Structure Impact a Ride-Hailing Business?. SAGE Publications: SAGE Business Cases Originals. Available At: https://sk.sagepub.com/cases/performance-incentives-gig-workers-employees-partners-ola-india?token=7413fd3d-d0bf-473e-9e02-81d8038c65e149ac2af0ad3c788b4108c64b02b1cc357d8371775d7a51450fe45f1cf46ccf59 [Accessed on: 12.01.24]
Journals
Afuah, A., 2020. Innovation management-strategies, implementation, and profits.
Agarwal, R., (2022). MARKETING IN THE NEXT NORMAL: A PRIMER. Fostering Resilient Business Ecosystems and Economic Growth: Towards the Next Normal, p.388.
Agarwal, S., Mani, D. and Telang, R., (2023). The impact of ride-hailing services on congestion: Evidence from Indian cities. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 25(3), 862–883.
Ali, B.J. and Anwar, G., 2021. Marketing Strategy: Pricing strategies and its influence on consumer purchasing decision. Ali, BJ, & Anwar, G.(2021). Marketing Strategy: Pricing strategies and its influence on consumer purchasing decision. International journal of Rural Development, Environment and Health Research, 5(2), pp.26-39.
Anirvinna, C. and Deshmukh, A.K., 2020. Pricing strategy of cab aggregators in India. Journal of Revenue and Pricing Management, 19, pp.248-254.
Anwar, S.T., (2023). The sharing economy and collaborative consumption: Strategic issues and global entrepreneurial opportunities. Journal of International Entrepreneurship, 21(1), 60–88.
Arora, S. and Kohli, C., (2023). The Rise of Surface Mobility in India. Disruptive Technologies in International Business: Challenges and Opportunities for Emerging Markets, p.61.
Athique, A. and Parthasarathi, V., 2020. Platform economy and platformization. Platform capitalism in India, pp.1-19.
Baierle, I.C., Benitez, G.B., Nara, E.O.B., Schaefer, J.L. and Sellitto, M.A., 2020. Influence of open innovation variables on the competitive edge of small and medium enterprises. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(4), p.179.
Baker, L., (2021). Everyday experiences of digital financial inclusion in India's ‘micro-entrepreneur’paratransit services. Environment and Planning A: Economy and Space, 53(7), pp.1810-1827.
Barbour, O. & Luiz, J. (2019). Embracing solutions-driven innovation to address institutional voids: The case of uber and the middle of the pyramid. California Management Review, 62(1), 31–52.
Cakranegara, P.A., Kurniadi, W., Sampe, F., Pangemanan, J. and Yusuf, M., 2022. The Impact Of Goods Product Pricing Strategies On Consumer Purchasing Power: A Review Of The Literature. Jurnal Ekonomi, 11(03), pp.1115-1120.
Clarke, R., (2020). RegTech opportunities in the platform-based business Sector.
D’Cruz, P. and Noronha, E., 2022. India’s platform economy experience. Platform Labour and Global Logistics: A Research Companion.
D’Souza, E. & Dev, P. (2019). Capital Market Predation in the Indian Internet Commerce Sector.
Dasgupta, P. and Deb, A., 2022. SERVICE PRICING CHALLENGES ON SHARED PLATFORM: UBER INDIA VS DIDI CHUXING. Management & Marketing Journal, 20(1).
Dsouza, W., (2019). Thomas, V.K., Kini, U.S. and Padhi, S., Is digitisation the key to opening blue oceans in India: A case study of OLA Cabs.
Fowler, J.G., Watson, A., Sen, S. and Sinha, N., (2023). Reconceptualizing marketing: an assessment of the marketing system in an emerging economy. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing.
Gala, K., (2023). Digital Davids, global Goliaths, and the Web3 sling. Business Horizons.
Gil-Gomez, H., Guerola-Navarro, V., Oltra-Badenes, R. and Lozano-Quilis, J.A., 2020. Customer relationship management: digital transformation and sustainable business model innovation. Economic research-Ekonomska istra�ivanja, 33(1), pp.2733-2750
Godbole, S. and Deshmukh, M.A., 2020. DEMOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION IMPACT ON CUSTOMER PERCEPTION TOWARDS CALL TAXI SERVICES IN TIER–-II TOWN OF NAGPUR IN MAHARASHTRA (INDIA). PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology, 17(7), pp.7496-7504.
Godbole, S. and Deshmukh, M.A., 2020. DEMOGRAPHIC SEGMENTATION IMPACT ON CUSTOMER PERCEPTION TOWARDS CALL TAXI SERVICES IN TIER–II TOWN OF NAGPUR IN MAHARASHTRA (INDIA). PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology, 17(7), pp.7496-7504.
Gugnani, R., (2022). Gig economy gets technology tick: stories from India. In Sustainability in the Gig Economy: Perspectives, Challenges and Opportunities in Industry 4.0 (pp. 243–254). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
Gulati, B. and Puri, V., (2022). Predation or Competition: Demystifying the Dilemma in Platform Markets. Competition Commission of India Journal on Competition Law and Policy, pp.167–194.
Harit, P., (2021). Autonomous Algorithmic Price Coordination. Available at SSRN 3968162.
Healy, J., Pekarek, A. and Vromen, A., 2020. Sceptics or supporters? Consumers’ views of work in the gig economy. New Technology, Work and Employment, 35(1), pp.1-19.
Huang, J., Henfridsson, O. and Liu, M.J., 2022. Extending digital ventures through templating. Information systems research, 33(1), pp.285-310.
Kadam, S.S. and Kadam, N., 2022. AN EFFECT OF BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY ON RIDE HAILING SERVICE PROVIDERS IN INDIA: A CASE STUDY OF UBER TAXI SERVICE PROVIDER.
Kadam, S.S. and Kadam, N., AN EFFECT OF BLUE OCEAN STRATEGY ON RIDE HAILING SERVICE PROVIDERS IN INDIA: A CASE STUDY OF UBER TAXI SERVICE PROVIDER.
Kathuria, R., Kedia, M. & Bagchi, K. (2021). India's platform economy and emerging regulatory challenges (No. 407). Working Paper.
Kumar, P. and Seshadri, U., 2021. Indian Retail Entrepreneu£and International Marketers: a Viable Business Ecosystem for Indian Start-Ups. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 25(2), pp.1-13.
Law, S.H., Sarmidi, T. and Goh, L.T., 2020. Impact of innovation on economic growth: Evidence from Malaysia. Malaysian Journal of Economic Studies, 57(1), pp.113-132.
Liu, Y. & Kim, D. (2022). Why did Uber China fail? Lessons from business model analysis. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(2), p.90.
Lozic, J., Cikovic, K.F. and Kecek, D., 2022. DIVERSIFYING INCOME OF THE UBER PLATFORM AS AN INTRODUCTION TO THE MATURE PHASE OF BUSINESS. Economic and Social Development: Book of Proceedings, pp.213-224.
More, S.V. and Rakshit, P., 2020. A REVIEW OF LITERATURE TO UNDERSTAND CAR RENTAL SERVICE MARKET. Advance and Innovative Research, p.281.
Muhiu, P., (2019). The Effect of sharing economy business model on customer value in Nairobi: a case of Uber (Doctoral dissertation, Strathmore University).
Mukerji, M. and Roy, P.S., 2019. Platform Interactions and Emergence of an Organizational Field: Case Study on Ola. Australasian Journal of Information Systems, 23.
Muralidhar, S.H., Bossen, C. & O’Neill, J. (2022). Between a Rock and a hard place: negotiating dependencies and precarity in the On-Demand economy. Computer Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW), 31(3), 443–486.
Mutogoh, H.I., 2021. Motivation in Sharing Economy-based Service Triads: Case of Uber Operations in Nairobi, Kenya (Doctoral dissertation, University of Nairobi).
OLIVEIRA, J.D.S., 2023. UBER’S PROFITABILITY: THE ELEPHANT IN THE ROOM.
Pitt, C.S., Bal, A.S. and Plangger, K., 2020. New approaches to psychographic consumer segmentation: exploring fine art collectors using artificial intelligence, automated text analysis and correspondence analysis. European Journal of Marketing, 54(2), pp.305-326.
Ploiesti, A. and Kurian, J.S., 2021. The future of shared economy: A case study on Airbnb. FIIB Business Review, 10(3), pp.205-214.
Rajesh, R., 2021. Study Of Customer Experience And Uses Of Uber Cab Services In Mumbai. International Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & Management, 10(6), pp.050-061.
Ramasamy, A., Muduli, K., Mohamed, A., Biswal, J.N. and Pumwa, J., 2021. Understanding Customer Priorities for Selection of Call Taxi Service Provider. Journal of Operations and Strategic Planning, 4(1), pp.52-72.
Raychaudhuri, T., (2020). Predatory Pricing and Market Determination in Non-Traditional Markets: An analysis of recent cases decided by the Competition Commission of India. Indian JL & Just., 11, p.31.
Ren, S., Hao, Y. and Wu, H., 2021. Government corruption, market segmentation and renewable energy technology innovation: Evidence from China. Journal of Environmental Management, 300, p.113686.
Riefa, C., (2021). Consumer law enforcement as a tool to bolster competition in digital markets: a case study on personalized pricing.
Roque, M.C.S.G., 2020. Uber, a path for profitability or a market misperception? (Doctoral dissertation).
Saqib, N. and Satar, M.S., 2021. Exploring business model innovation for competitive advantage: a lesson from an emerging market. International Journal of Innovation Science, 13(4), pp.477-491.
Saxena, D., Muzellec, L. and Trabucchi, D., 2020. BlaBlaCar: Value creation on a digital platform. Journal of Information Technology Teaching Cases, 10(2), pp.119-126.
Saxena, U., (2019). UBERIFICATION: A DISRUPTIVE INNOVATION IN RIDESHARING REVOLUTION.
Sehrawat, U., Sawhney, N., Yeleswarapu, T. & Rangaswamy, N. (2021). The Everyday HCI of Uber Drivers in India: A Developing Country Perspective. Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, 5(CSCW2), pp.1–22.
Sharmin, F., (2021). EFFECT OF CORONA VIRUS IN UBER BUSINESS MODEL: EVIDENCE FROM SOUTH ASIA.
Sinha, P.K., Agarwal, A.M. & Singh, K. (2021). Suggested business model for start-ups in achieving goals of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Subhadarsi, A., 2023. Web3 and Business to Consumer Electronic Commerce: Indian Competition Law Paradigm. European Economic Letters (EEL), 13(3), pp.1170-1177.
Surie, A., (2020). On-demand platforms and pricing: how platforms can impact the informal urban economy, evidence from Bengaluru, India. Work Organisation, Labour & Globalisation.
Tan, Z.M., Aggarwal, N., Cowls, J., Morley, J., Taddeo, M. & Floridi, L. (2021). The ethical debate about the gig economy: A review and critical analysis. Technology in Society, 65, p.101594.
Tatarauca, L.M., 2022. A transaction cost approach to the gig economy: the case of India.
THAPA, G., (2020). Consumer Behaviour On Online Ride Hailing Apps In India. PalArch's Journal of Archaeology of Egypt/Egyptology, 17(12), 1176–1189.
Thombre, K.A. and Sannake, A.C., CAB IN INDIA: A CASE STUDY OF OLA AND UBER.
Tong, T., Dai, H., Xiao, Q. and Yan, N., 2020. Will dynamic pricing outperform? Theoretical analysis and empirical evidence from O2O on-demand food service market. International Journal of Production Economics, 219, pp.375-385.
Tyagi, H., (2022). RESEARCH ON BUYING AND SELLING PATTERN OF PRE-OWNED CARS IN INDIA (Doctoral dissertation).
Van Der Kroft, A. and Neubert, M., 2020. Digital internationalisation of ride Hailing firms. In 13th Annual Conference of the EuroMed Academy of Business (pp. 1196-1207).
Vatal, A., 2023. Impact of Uber on the Autorickshaw Industry–Consumer Perspectives in Pune. International Journal of Research in Engineering, Science and Management, 6(3), pp.135-143.
Velmurugan, J.S., Shruthi, R. and Rajkamal, S.V., 2019. Customer perception and problems towards OLA services in smart cities with reference to Salem. Rupkatha Journal on Interdisciplinary Studies in Humanities, 11(3).
Venkatesh, D.N., 2022. Performance Incentives for Gig Workers, Employees, and Partners at Ola in India: How Does Compensation Structure Impact a Ride-Hailing Business? SAGE Publications: SAGE Business Cases Originals.
Vijay, T.S., Prashar, S. and Sahay, V., 2020. Ola acquired TaxiForSure: post-takeover dilemma. Vikalpa, 45(1), pp.42-50.
Vinod, P.P. & Sharma, D. (2021). COVID-19 impact on the sharing economy post-pandemic. Australasian Accounting, Business and Finance Journal, 15(1), 37–50.
Wang, H. and Yang, H., 2019. Ridesourcing systems: A framework and review. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 129, pp.122-155.
Wilson, A. & Mason, B. (2020). The coming disruption–The rise of mobility as a service and the implications for government. Research in transportation economics, 83, p.100898.
Wu, Q., Yan, D. and Umair, M., 2023. Assessing the role of competitive intelligence and practices of dynamic capabilities in business accommodation of SMEs. Economic Analysis and Policy, 77, pp.1103-1114.
Wu, Q., Zhang, H., Li, Z. and Liu, K., 2019. Labour control in the gig economy: Evidence from Uber in China. Journal of Industrial Relations, 61(4), pp.574-596.
Wu, T., Zhang, M., Tian, X., Wang, S. & Hua, G. (2020). Spatial differentiation and network externality in pricing mechanism of online car hailing platform. International Journal of Production Economics, 219, pp.275-283.
Yadegaridehkordi, E., Nilashi, M., Nasir, M.H.N.B.M., Momtazi, S., Samad, S., Supriyanto, E. and Ghabban, F., 2021. Customers segmentation in eco-friendly hotels using multi-criteria and machine learning techniques. Technology in Society, 65, p.101528.
Zheng, H., (2022). Analysis of reasons for the failure of enterprise localization and suggestions for development in the future: the example of Uber China. Highlights in Business, Economics and Management, 4, pp.241–250.
Zhou, Y., Yang, H., Ke, J., Wang, H. and Li, X., 2020. Competitive ride-sourcing market with a third-party integrator. arXiv preprint arXiv:2008.09815.
Article
Chi, H.R., Ho, H.P. and Lin, P.K., 2022. Survival strategies of the sharing economy from the pandemic to a new normal: A dynamic capabilities approach. Managerial and Decision Economics, 43(7), pp.3219-3234. Available at: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mde.3592 [Accessed on: 3.1.2024]
Tham, A. and Ogulin, R., 2023. May the fourth (industrial) revolution be with you: Value convergence within Uber’s sharing economy. International Journal of Innovation and Technology Management, 20(07), p.2140013. Available at: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/abs/10.1142/S0219877021400137 [Accessed on: 12.01.24]
Website
Openurl.ebsco.com, (2022), Available at: https://openurl.ebsco.com/EPDB%3Agcd%3A3%3A3079811/detailv2?sid=ebsco%3Aplink%3Ascholar&id=ebsco%3Agcd%3A158321754&crl=c openurl.ebsco.com
Researchgate.net, 2020-pricing strategy of cab aggregato£in India Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332592833_Pricing_strategy_of_cab_aggregators_in_India [Accessed on: 3.1.2024]